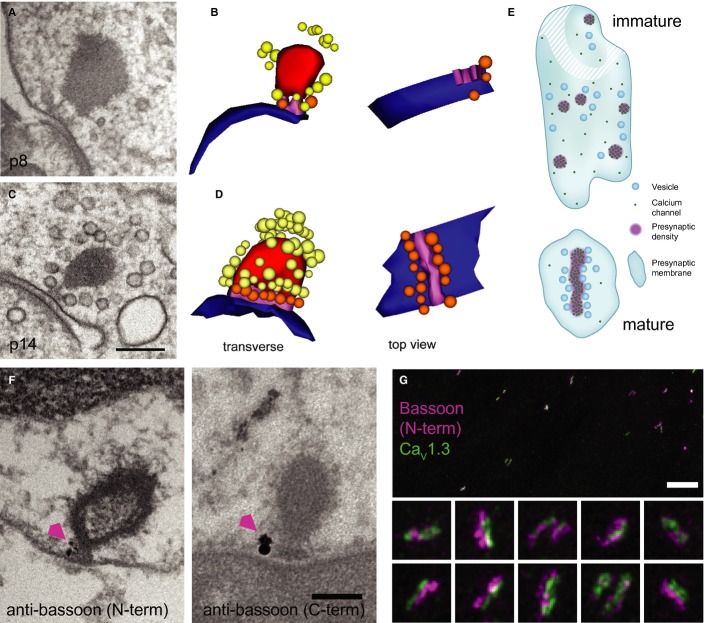
Nanoanatomy of IHC AZs.
TEM of an immature IHC ribbon synapse using high-pressure freezing and freeze substitution (HPF/FS).
Corresponding serial 3D reconstruction of (A), showing the immature ribbon connected via two rootlets to the presynaptic membrane. For color code see (D)
Representative TEM of a mature ribbon, connected with one continuous presynaptic density to the membrane, as demonstrated in the 3D reconstruction in (D).
3D reconstruction: ribbon: red; AZ membrane: blue; rootlet (immature)/presynaptic density (mature): magenta; membrane-proximal SVs: orange; ribbon-associated SVs: yellow.
Schematics of immature (top) and mature (bottom) AZs inspired by exemplary 3D reconstructions and STED imaging of CaV1.3 immunofluorescence. Ca2+ channels formed small clusters and vesicles were less organized at the immature AZ. Stripe-like Ca2+-channel cluster with vesicles positioned regularly along each side at the mature AZ.
Pre-embedding immunogold labeling for bassoon (arrowhead) was detected at the ribbon-anchoring presynaptic density of mature ribbons. Two primary antibodies specific to the N-terminal or C-terminal of bassoon, respectively, were used (see Materials and Methods). Scale bar, 200 nm.
STED image of immunolabeled bassoon (magenta) and CaV1.3 channel clusters (green) in mature IHCs: stripe-like morphology and closely aligned immunofluorescence of bassoon and CaV1.3 reminiscent of the presynaptic density reconstructed from TEM (D). The image is a maximum intensity projection after smoothing with a Gaussian (σ = 1 pixel) in ImageJ. The color lookup was chosen to optimize contrast and visibility of dimmer structures. Pixel size, 20 nm. Scale bar, 2 μm. Insets, 700 × 700 nm.