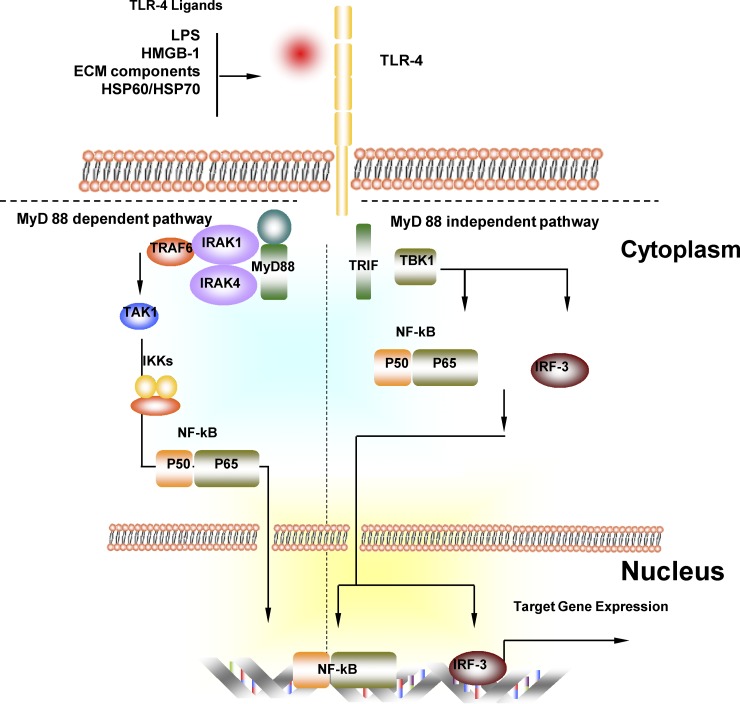
Fig. 2.
Myeloid differentiation primary-response protein 88 (MyD88)-dependent and MyD88-independent TLR-4 signaling pathway. In the MyD88-dependent pathway, activation of TLR-4 through TLR-4 ligand recruits and activates MyD88 and then IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-4. IRAK-4 phosphorylates IRAK-1, which recruits TNF-receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). TRAF6, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (UEV1A, UBC13) and binding proteins (TAB1, TAB2) interact to activate TGF-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1). Activation of TAK1 leads to the activation of the inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB kinase (IKK) complex, which releases NF-κB from its inhibitor and promotes its translocation into the nucleus. NF-κB is then translocated into the nuclear and initiates gene expression. In the Myd88-independent signaling pathway, TLR-4 activation leads to TRIF activation. TRIF recruits IKKε, which possibly forms a complex with TBK1 to activate transcription factors NF-κB and IFN-regulatory factor 3 (IRF-3). Gene expression is then initiated.