Figure 1.
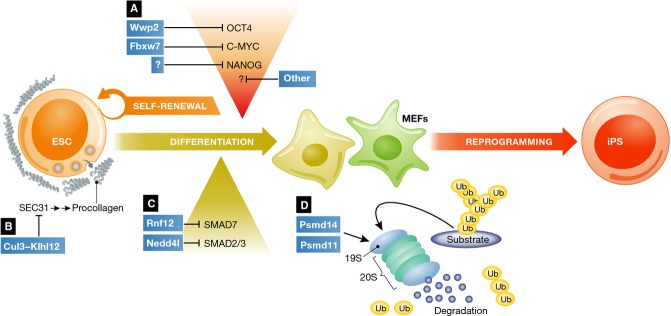
Ubiquitylation regulates ESC pluripotency, differentiation and iPS cell generation.
(A) The E3 ligases SCFFbxw7 and Wwp2 regulate core transcription factor—such as c-Myc and Oct4—abundance and functions in ESCs. Additional enzyme–substrate pairs may control transcriptional regulation of ESCs. SCFFbxw7 controls cellular reprogramming and iPS generation, in addition to differentiation, through c-Myc stabilization. (B) Cul3-Klhl12 ubiquitylates Sec31, regulating COPII vesicle size and procollagen export to the extracellular matrix. (C) Ubiquitylation regulates signaling components in ESCs. Nedd4l and Rnf12 regulate Smad2/3 and Smad7 levels, respectively. (D) Enzymatic functions of the proteasome control self-renewal and differentiation of ESCs, as well as cellular reprogramming. Psmd14 and Psmd11 regulate 19S regulatory particle activity and assembly, respectively.
