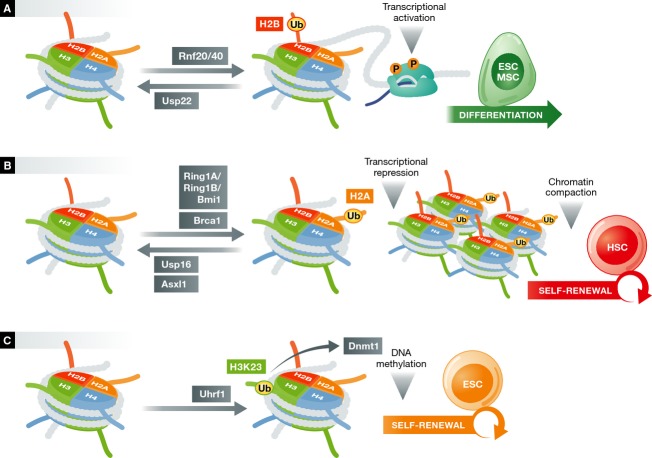
Figure 4.
Regulation of chromatin functions in stem cells by ubiquitylation.
(A) H2B ubiquitylation marks open chromatin and facilitates transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II. The E3 ligases RNF20 and RNF 40, and the DUB USP22, control H2B-Ub deposition and transcriptional activation, resulting in ESC and MSC differentiation. (B) H2A ubiquitylation is deposited by either the PRC1 complex, which consists of RING1A/RING1B/BMI1- or the E3 ligase BRCA1, and is associated with transcriptional repression and chromatin compaction. The DUBs USP16 and Asxl1 can reverse this process, regulating the functions of hematopoietic and mammary stem cells. (C) H3K23 ubiquitylation is catalyzed by the E3 ligase Uhrf1. This recruits Dnmt1, which maintains DNA methylation at sites of replication.