Figure 5.
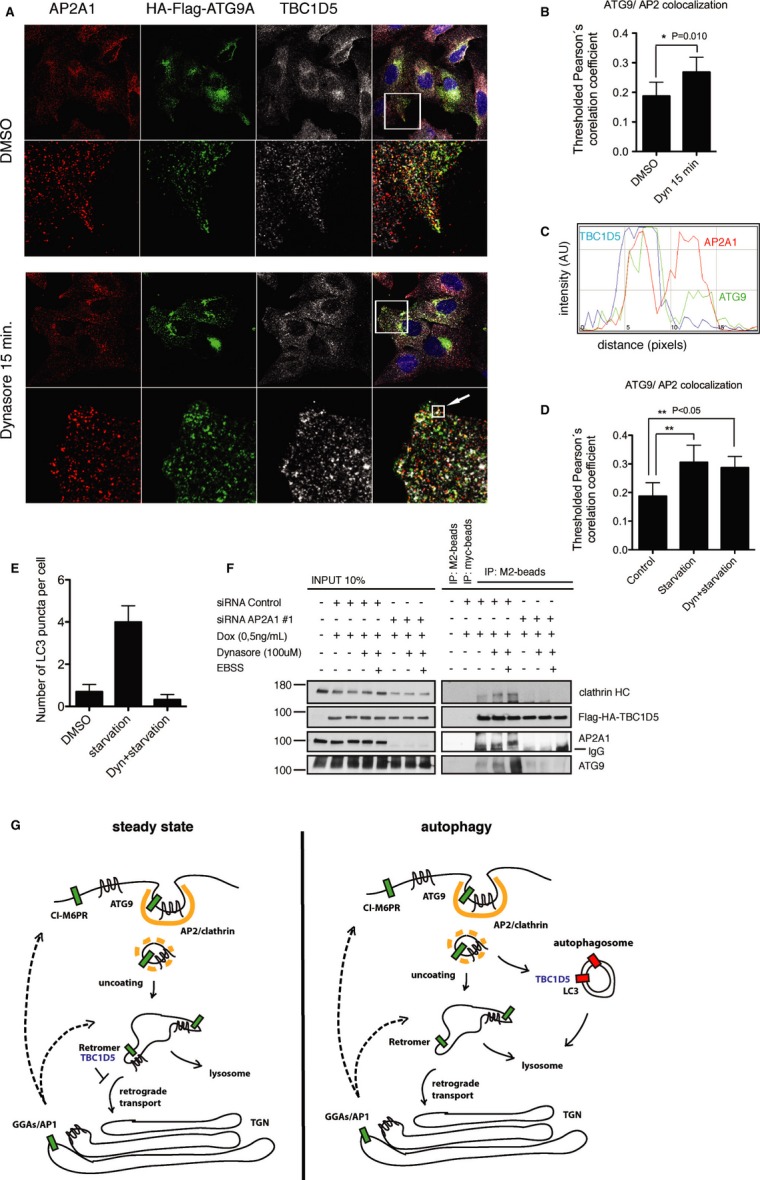
- U2OS cells stably expressing HA-Flag-ATG9A treated with DMSO or Dynasore (100 μM) 15 min, fixed and immunostained with anti-HA and anti-TBC1D5 antibodies.
- Quantification of ATG9A and AP2 co-localization from experiment in (A), pictures from 3 independent experiments were analyzed and co-localization quantified, statistics is calculated as described in Supplementary Materials and Methods.
- RGB-line profile across the vesicle indicated with arrow in (B); red—AP2; green—ATG9A; blue—TBC1D5.
- Quantification of ATG9A and AP2 co-localization. Cells were starved in EBSS media (45 min) or pretreated with Dynasore (15 min) and subsequently starved for 45 min in combination with Dynasore. Control cells were treated with DMSO.
- Quantification of LC3 puncta in cells stably expressing HA-Flag-ATG9A, treated and presented as in (D). 100 cells were quantified in 3 independent experiments.
- T-REx HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA Control oligo or siRNA oligo#1 targeting AP2A1 (40 nM). 72 h post-transfection, expression of HA-Flag-TBC1D5 was induced with doxycycline (50 ng/ml), and 96 h post-transfection cells were treated with Dynasore for 15 min, or pretreated with Dynasore and subsequently starved in combination with Dynasore for additional 45 min. Cells were lysed in co-immunoprecipitation buffer, and lysates were incubated with Myc antibody or M2 antibody coupled with agarose overnight at 4°C. Beads were washed 3 times with incubation buffer and subjected to SDS–PAGE.
- Proposed model for AP2 and TBC1D5 role in ATG9 trafficking toward autophagosomes. At steady state ATG9 traffics from Golgi to the endosomes and to the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane fraction gets internalized via AP2. During autophagy ATG9-AP2 vesicles redistribute toward autophagosomes via interaction of TBC1D5 with AP2 and LC3.
Data information: Bar graphs (B, D, E), mean ± s.d. n = 3, unpaired two-tailed t-test, P-values: ns P > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.
