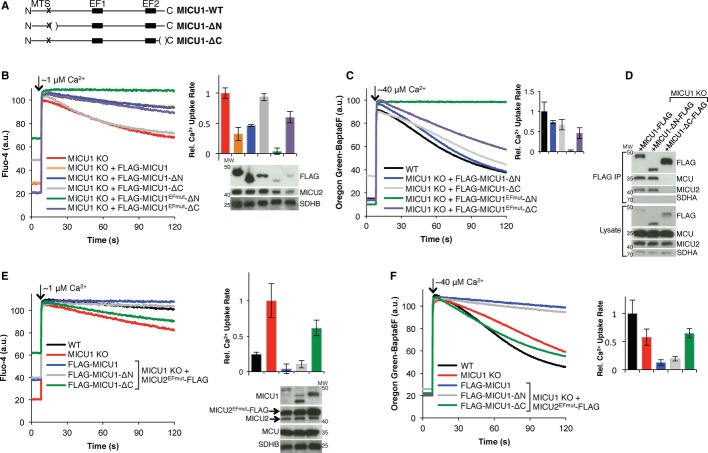
C-terminal domain of MICU1 is important for its function.
A Schematic showing the MICU1 truncation mutants used. N and C represent the N-and C-termini, respectively; MTS labels the predicted mitochondrial targeting signal; EF1 and EF2 label the two canonical EF hand domains; parentheses show deleted residues.
B, C Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake in digitonin-permeabilized HEK-293T MICU1 KO cells stably expressing MICU1, MICU1-ΔN, MICU1EFmut-ΔN, MICU1-ΔC, or MICU1EFmut-ΔC given a (B) ˜1 μM or (C) ˜40 μM Ca2+ pulse, monitoring extramitochondrial [Ca2+]. Representative traces are shown on the left, and the quantification of uptake rate from linear fits (50–60 s, n ≥ 3) is on the right. Immunoblots of whole-cell lysates for the corresponding cells are shown under the respective bar graph lane.
D FLAG immunoprecipitation for FLAG-tagged MICU1, MICU1-ΔC, or MICU1-ΔN. Eluates and lysates are immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
E, F Response of digitonin-permeabilized HEK-293T MICU1 KO cells stably expressing MICU2EFmut in addition to MICU1, MICU1-ΔN, or MICU1-ΔC to a (E) ˜1 μM or (F) ˜40 μM Ca2+ pulse, monitoring extramitochondrial [Ca2+]. Representative Ca2+ uptake traces are shown on the left, and quantification of uptake rate from linear fits (50–60 s, n ≥ 3) is on the right. Immunoblots of whole-cell lysates for the corresponding cells are shown under the respective bar graph lane.