Fig. 5.
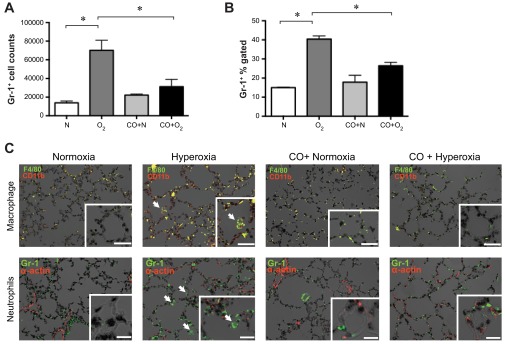
Hyperoxic exposure induces neutrophilic infiltration into neonatal lungs that is ameliorated by CO-induced treatment. A and B: high Gr-1+, CD45+ cells, representing infiltrating neutrophils, were measured by flow cytometry. Treatment of hyperoxia-exposed mice with exogenous CO decreased the number of CD45 high Gr-1+ cells. Data from 14-day exposures are shown (A, number of cells per 106 events; B, percentage of CD45+ cells). C: immunofluorescent stains of 14-day lung sections from normoxia-, hyperoxia-, CO + normoxia-, and CO + hyperoxia-exposed mice. Top: neutrophil panels show Gr-1 (green, arrows) and α-actin (red). Bottom: macrophage staining panels include F4/80 (green) and CD11b (red). Colocalization (yellow) indicates CD11b-positive macrophages (arrows). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (black). Original magnification is ×200, scale bar = 10 μm. Insets: high-magnification views (×400).
