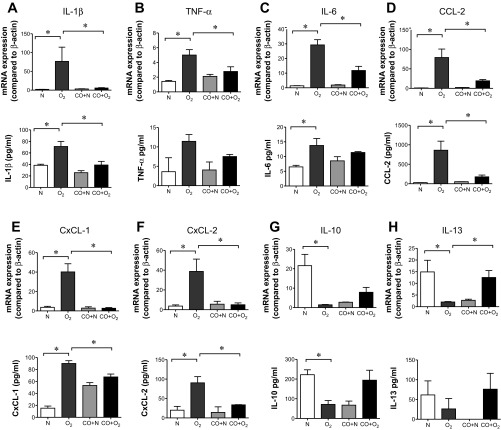
Fig. 7.
Exogenous CO administration regulates the expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines under hyperoxic conditions. mRNA and protein levels were measured by quantitative PCR and multiplex immune assay at 14 days postexposure. A–F: hyperoxia increased the mRNA and protein expression of IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, CCL-2, IL-10, IL-13, CxCL-1, and CxCL-2. CO administration significantly reduced IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, CCL-2, CxCL-1, and CxCL-2 mRNA expression as well as IL-1β, CCL-2, CxCL-1, and CxCL-2 protein expression. G and H: IL-10 and IL-13 were downregulated by hyperoxic treatment and increased with CO exposure. The data pool is at least 3 independent experiments (means ± SE, n = 10–18 animals per group for mRNA analysis, n = 4 per group for protein analysis, *P <0.05, ANOVA).