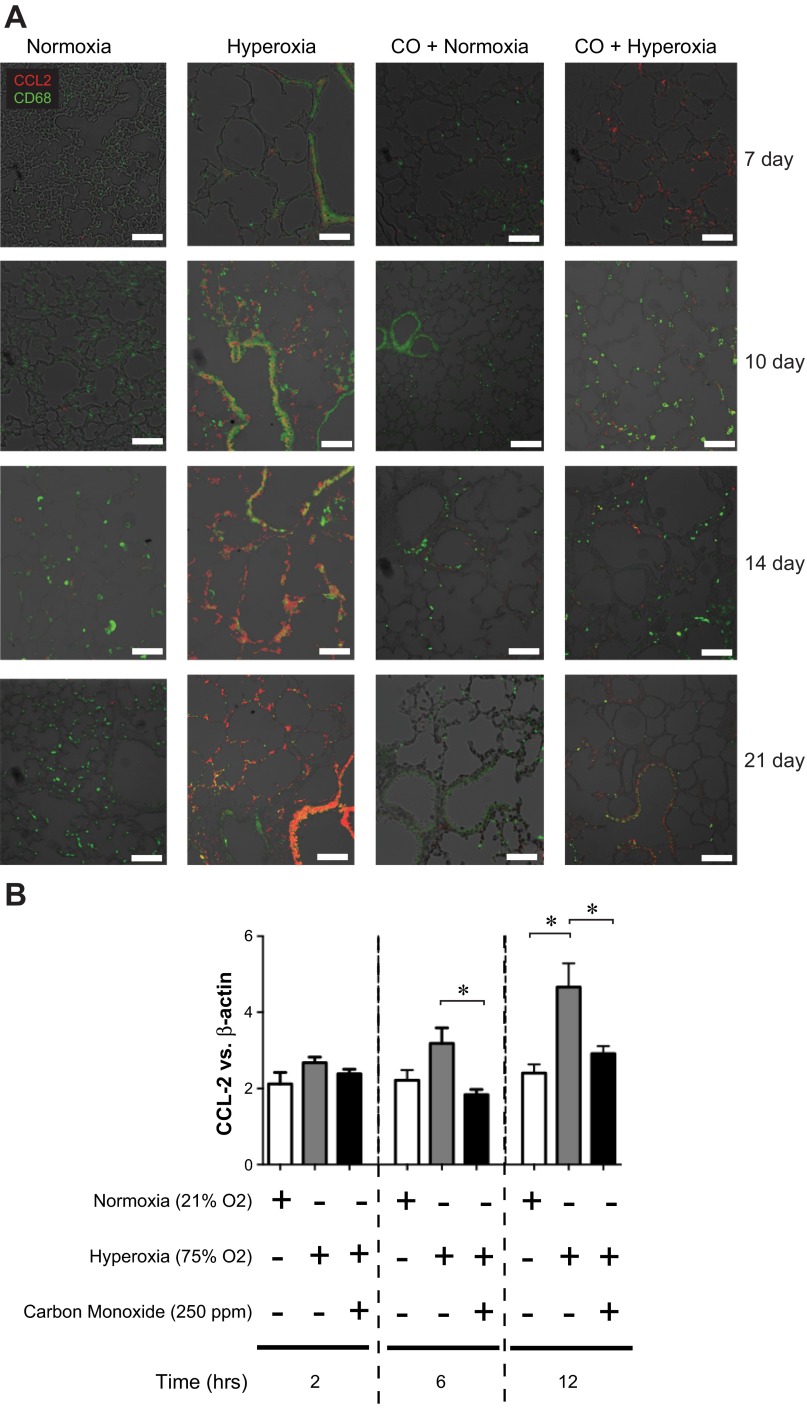
Fig. 8.
Hyperoxia exposure is associated with an increase in respiratory epithelial cell CCL2 expression. Lung sections were stained for CCL2 (red) or CD68 (green); colocalization appears yellow. Compared with normoxia-exposed mice, hyperoxia-exposed mice show an increase in CCL2 expression primarily in the epithelium as well as an increase in CD68-positive macrophages. Episodic CO treatment the presence of hyperoxic exposure suppressed CCL2 expression. Lung sections from 7, 10, 14, and 21 days of exposure are shown (line segment = 50 μm, results are typical of 3 individual experiments). B: murine type II alveolar epithelial cells were exposed to 250 ppm CO or room air in the absence or presence of high oxygen tension (>95% O2) for a duration of 2, 6, or 12 h. CCL2 mRNA expression was increased by hyperoxia and attenuated by CO. Group mean data for CCL2 mRNA expression are presented (means ± SE, n = 3, *P < 0.05, ANOVA).