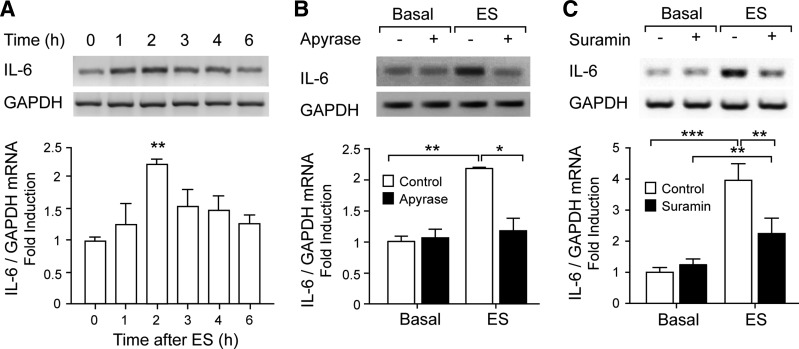
Fig. 1.
Electrical stimulation (ES) induced ATP-dependent IL-6 expression in rat myotubes. Rat myotubes were electrically stimulated (45 Hz, 400 pulses, 1 ms each). Total RNA was isolated at the indicated times. IL-6 mRNA expression was assessed by conventional semiquantitative RT-PCR. A: IL-6 mRNA levels increase with ES. B: extracellular nucleotide metabolization abolished IL-6 expression evoked by ES. IL-6 expression increased 2 h after ES, and this increase was blocked after ATP metabolization using 2 U/ml apyrase for 30 min prior to and during the protocol. C: nucleotide receptor blockade strongly reduced IL-6 expression evoked by ES. The general P2Y/P2X antagonist suramin (100 μM), incubated for 30 min prior to and during the protocol, significantly reduced IL-6 expression increased 2 h after ES. Top: representative agarose gels for RT-PCR products from IL-6 mRNA amplifications with their corresponding GAPDH control. Bottom: correspondence to intensity quantization of each IL-6 band normalized to GAPDH expression, presented as fold increase of untreated control cells (means ± SE; n = 3–6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison test.