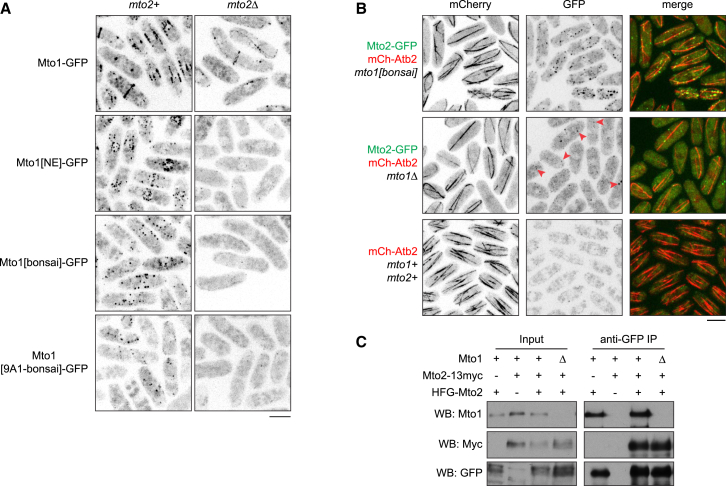
Figure 3.
Assembly of Multimeric Puncta In Vivo
(A) Images showing puncta of Mto1[NE]-GFP, Mto1[bonsai]-GFP, and Mto1[9A1-bonsai]-GFP in wild-type backgrounds (mto2+) and absence of puncta in mto2Δ backgrounds. Mto1[9A1-bonsai]-GFP puncta diffuse rapidly but are prominent in movies (see Movie S3). Full-length Mto1-GFP displays a weak but still detectable signal in mto2Δ backgrounds, due to its intrinsic ability to enrich at many MTOC sites ([9]; see also Figure 1A).
(B) Mto2-GFP puncta together with mCherry-tubulin (mCh-Atb2) in mto1[bonsai] and mto1Δ cells. Arrows indicate examples of puncta in mto1Δ cells, which are relatively faint and seen more easily in movies or when Mto2-GFP is overexpressed (see Movie S5 and Figure S3E). Wild-type cells (mto1+ mto2+) provide a negative control for GFP fluorescence.
(C) Mto2-13myc is coimmunoprecipitated with 6His-FLAG-GFP-Mto2 (HFG-Mto2), in both mto1+ and mto1Δ backgrounds. Western blots were probed with antibodies against GFP, Myc, and Mto1. Scale bars, 5 μm.