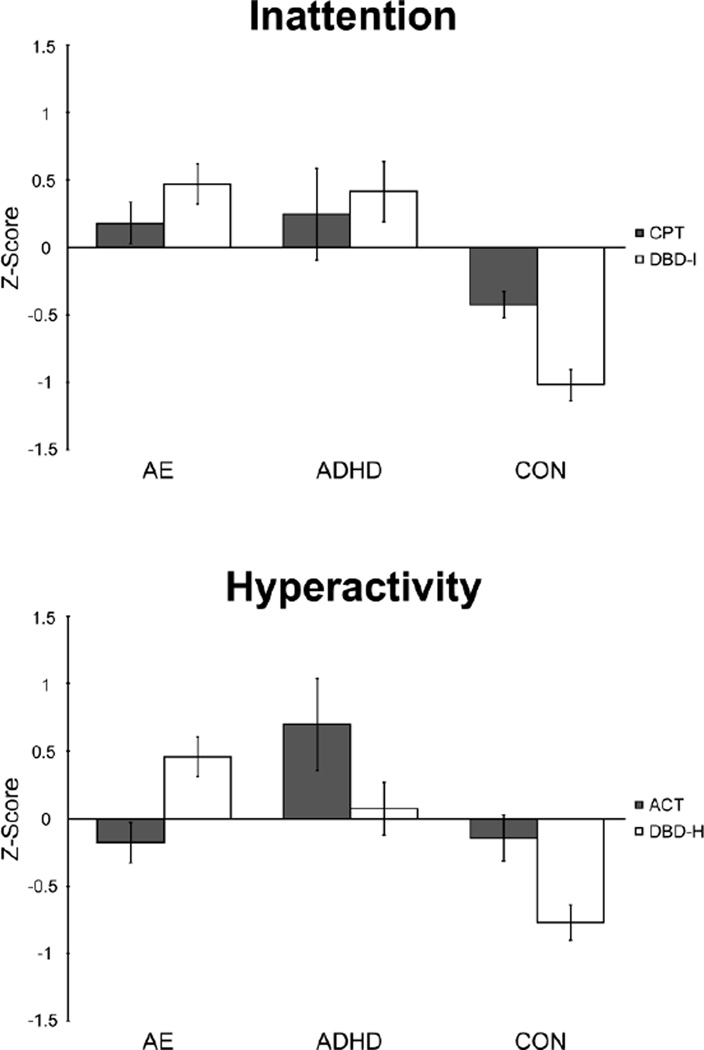
Figure 1.
Average scores for parent-reported and laboratory measures of inattention and hyperactivity for the alcohol-exposed (AE), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and control (CON) groups. Positive scores indicate higher median activity for Actigraph (ACT), increased number of omission errors (CPT), and higher symptom counts for parent-reported hyperactivity and inattention (DBD-H, DBD-I). Individual subject data were converted to z-scores, based on the entire study sample and are presented as mean z-score +/− standard error.