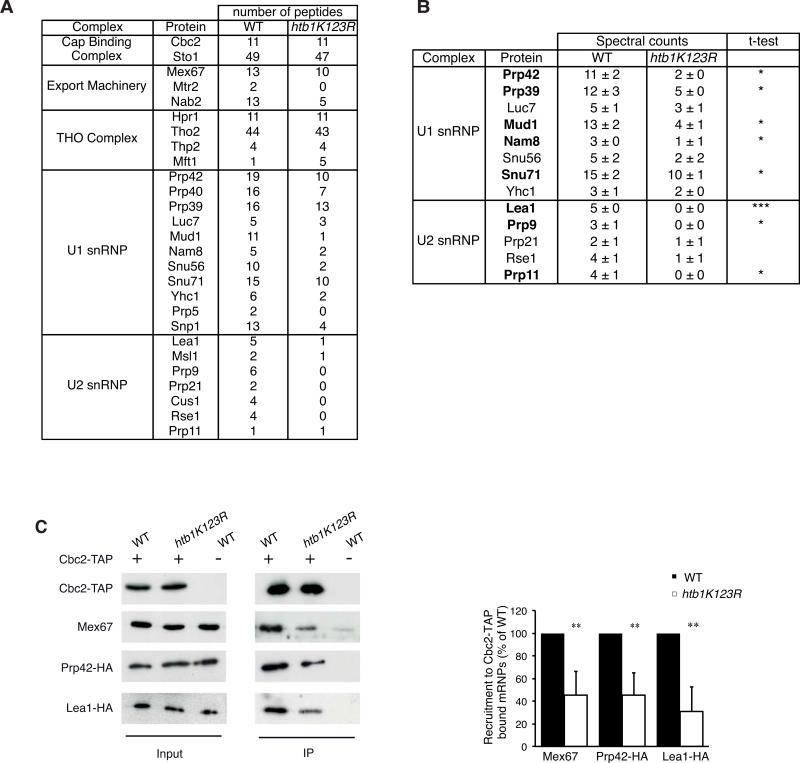
Figure 3. Preventing ubiquitylation of H2B alters the recruitment of early splicing factors to CBC-associated mRNPs.
(A) Nuclear mRNPs were purified from Cbc2-TAP-tagged WT or htb1K123R cells after a 3-hour shift to 39°C and associated proteins were analyzed by MS-MS after SDS-PAGE. In order to highlight relative differences in the protein composition, the number of unique peptides for each indicated protein has been considered as index of abundance (Merz et al., 2007). Complete identification of the CBC proteomes is shown in Table S4. (B) Components of the U1 and U2 snRNPs associated with nuclear mRNPs were semi-quantified using a spectral counting approach. The mean ± SD of spectral counts corresponding to three injections are indicated. Significance of the differences observed between both strains was evaluated using Student t-test (*P 0.01–0.05; ***P <0.001). Significant differences are indicated in bold. (C) Nuclear mRNPs were purified from WT or htb1K123R cells expressing Cbc2-TAP and Prp42-HA or Lea1-HA. Co-purifying proteins were detected by Western Blot with anti-HA or anti-Mex67 antibodies (left panel). The ratio of mRNP-associated proteins relative to the WT cells and to the immuno-purified Cbc2-TAP was determined from at least 3 independent experiments (mean ± SD) (right panel). Significance of the differences observed between both strains was evaluated using Student t-test (**P 0.001–0.01).