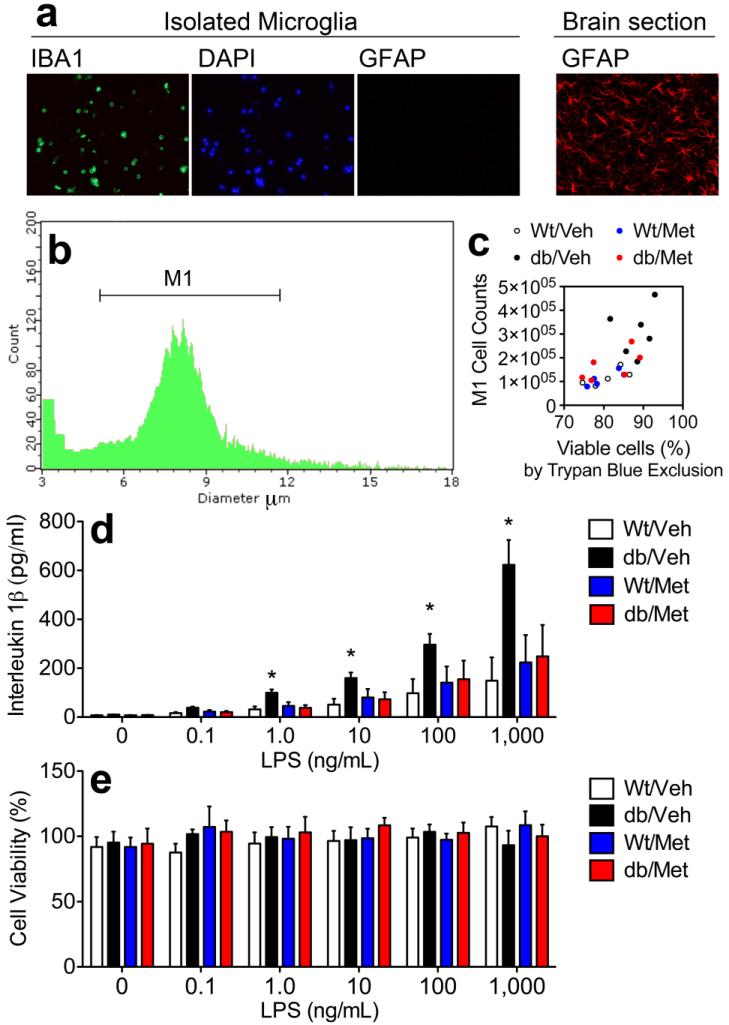
Figure 6. Ex vivo stimulation of microglia reveals corticosteroid-dependent sensitization to an immune challenge in db/db mice.
(A), Cells collected at the 70%/30% interface express the microglial marker IBA1, but do not express the astroglial marker GFAP. (B), Automated measurement of cell number and cell diameter easily distinguishes between microglia and debris. (C), Automated cell counts restricted to expected diameter of isolated microglia (M1 region) are positively correlated with cell viability assessed through Trypan Blue exclusion. (D), Levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin 1beta were quantified by ELISA in media following 18hr LPS stimulation. Microglia from vehicle-treated db/db mice had a significantly lower threshold for release of IL1beta, relative to wildtype mice, while microglia from metyrapone-treated db/db mice were indistinguishable from wildtype controls. (E), These patterns could not be explained by differences in cell viability, as analysis of cell viability by XTT assay revealed no differences between groups. For all graphs, asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance at p<0.05 following 2×2 repeated measures ANOVA, and error bars depict the s.e.m.