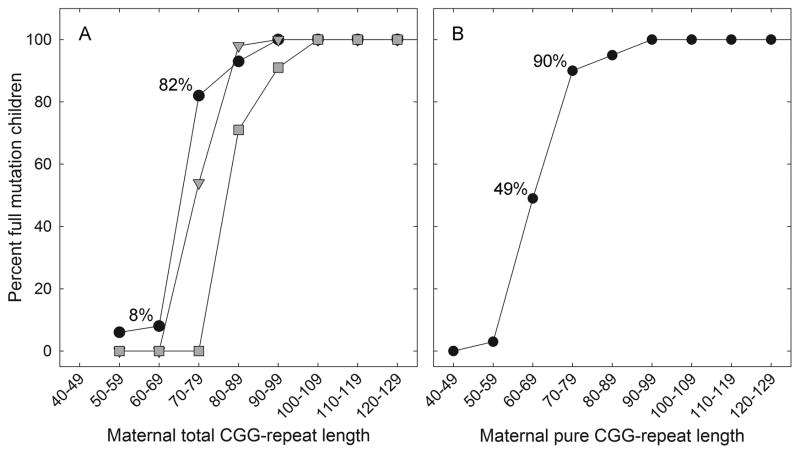
Figure 2.
Risk of expansion to a full mutation during maternal transmission. (A) Percent of alleles that expanded to a full mutation as a function of total CGG repeat length, for 0 (solid circle), 1 (gray triangles), or 2 (gray squares) AGG interruptions. (B) Percent full mutation expansions as a function of pure CGG repeat length within alleles that have either 0, 1, or 2 AGGs.