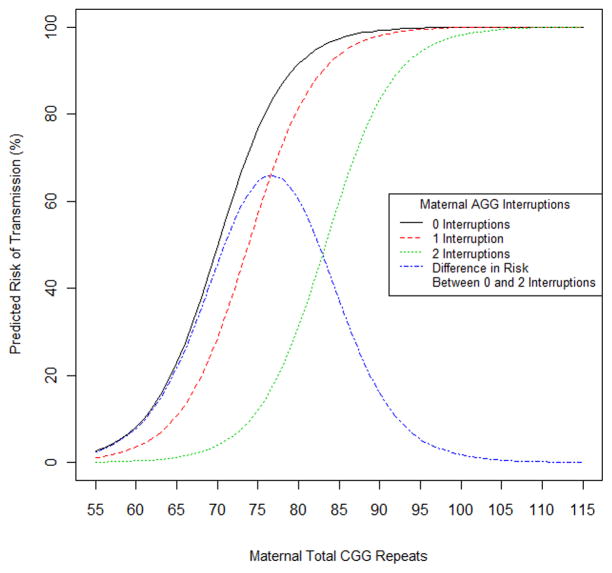
Figure 3.
Predicted risk of expansion during transmission by maternal total CGG repeat and AGG interruptions. Risk of expansion decreases when the number of AGG interruptions increases, for the same total CGG repeat length. The differential risk between one and two AGG interruptions is highest between 75 and 80 total CGG repeats.