Figure 8. NDP52 plays an important role in the clearance of phosphorylated tau.
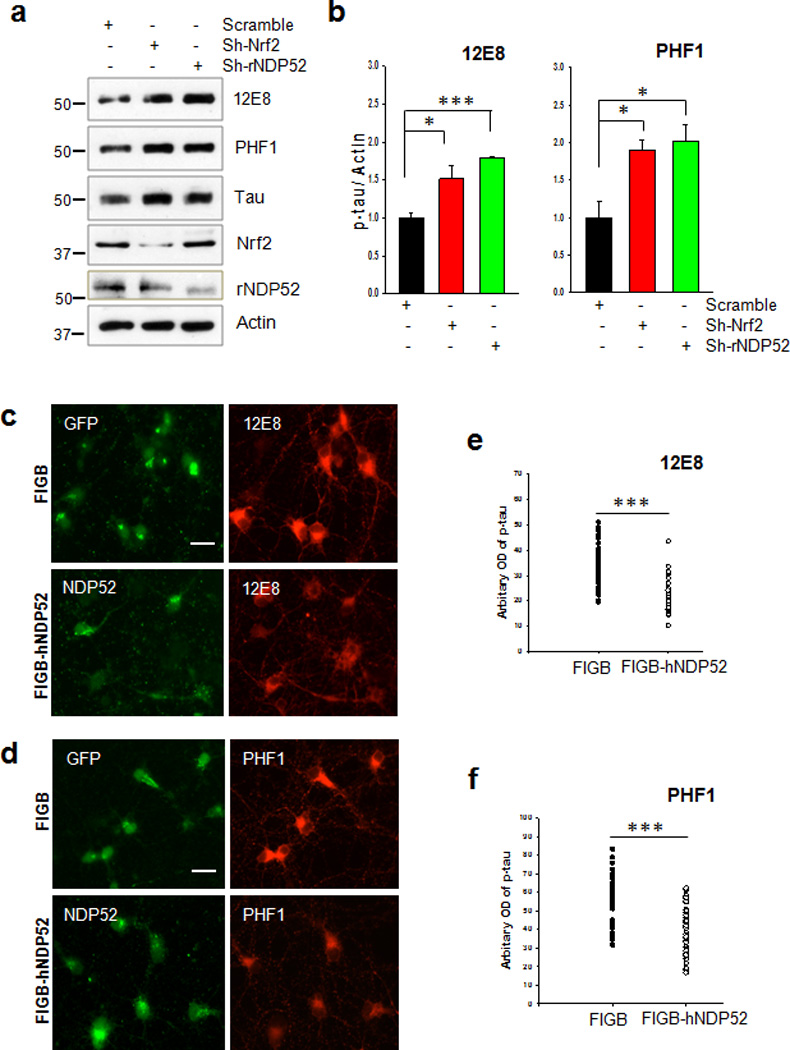
(a) Primary cortical neurons were transduced with lentivirus expressing sh-RNA for Nrf2 or rat NDP52 (rNDP52), or a scrambled sh-RNA at DIV 1, and maintained until DIV 6. The levels of tau phosphorylated at Ser262/Ser356 and Ser396/Ser404 were analyzed by immunoblotting using 12E8- and PHF1-specific antibodies, respectively. Total tau was detected with a polyclonal tau-specific antibody (Tau). The relative molecular masses (kD) are indicated to the left of each blot. (b) Bar graph of the relative optical density of phosphorylated tau normalized to actin. Data shown are mean±SE of three independent experiments and were analyzed using Student’s t test. (*, p<0.05; ***, p<0.001) (c, d) Primary cortical neurons were transduced with a control lentivirus (FIGB) or with one expressing human NDP52 (hNDP52) at DIV 1. To induce autophagy, trehalose (150 mM) was added at DIV 5 and the neurons incubated for 24 h (DIV 6). Primary cortical neurons were fixed with 4% PFA, and stained with the 12E8 or PHF1 antibodies. The optical density of tau phosphorylated at Ser262/Ser356 (12E8). Scale bar = 20 µm. (e) and Ser396/Ser404 (PHF1) (f) in the soma of approximately 30 neurons randomly chosen was analyzed with the ImageJ program. Data were analyzed using Student’s t test (***, p<0.001)
