Figure 9. The SKICH domain of NDP52 interacts with tau.
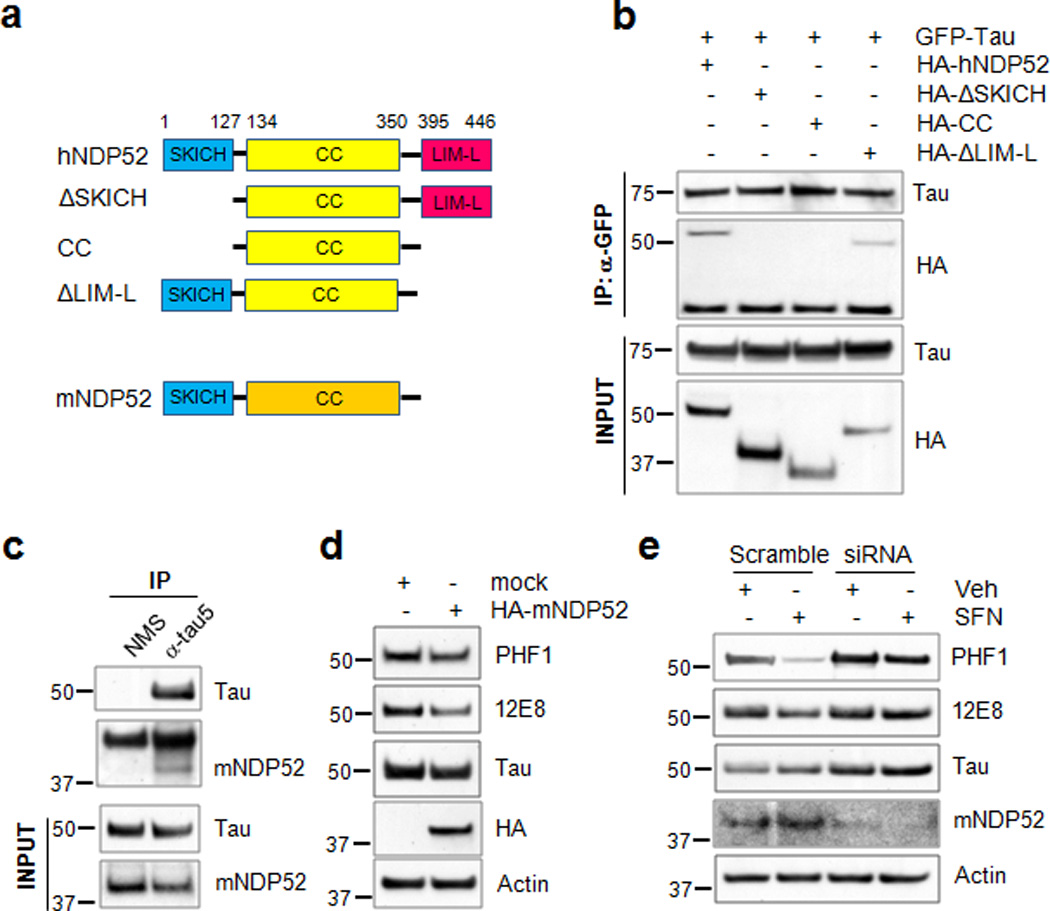
(a) Schematic diagram of human NDP52, the domain-deleted constructs and mouse NDP52. (b) Naïve cortical cells were co-transfected with the plasmids expressing HA-hNDP52 or HA-tagged domain-deleted mutants of human NDP52 together with GFP-tau. Twenty-four hours later cell lysates were prepared and transfected tau was immunoprecipitated and blots probed for both the HA-hNDP52 constructs and GFP-tau. Homogenates (input) used for co-immunoprecipitation were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA or a polyclonal tau-specific antibody (Tau). (c) Stably transfected CN1.4 cortical neurons were maintained in the presence of doxycycline (1 µg/ml) to induce the expression of tau for 24 h. Homogenates from CN1.4 cortical neurons were used for the co-immunoprecipitation of mouse NDP52 (mNDP52) using a Tau5 antibody. Co-precipitation of mNDP52 was examined by immunoblotting using anti-NDP52 antibody. Input of the homogenates used for co-immunoprecipitation was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-NDP52 or Tau antibody. (d, e) CN1.4 cortical neurons were transfected with the mock or HA-mNDP52 plasmid (d) or with mNDP52 siRNA or scramble RNA as a control (e). The cells transfected with siRNA or scramble RNA were treated with SFN (10 µM) for 24 h. The levels of tau phosphorylated at Ser262/Ser356 and Ser396/Ser404 were analyzed by immunoblotting using 12E8- and PHF1-specific antibodies, respectively. Total tau was detected with a polyclonal tau-specific antibody (Tau). The relative molecular masses (kD) are indicated to the left of each blot.
