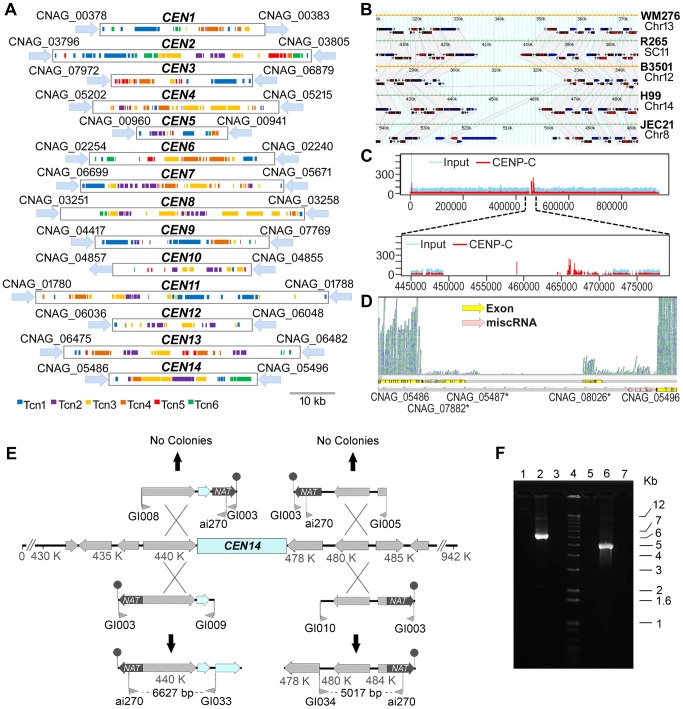
Figure 9. Organization of the centromeres in C. neoformans strain H99 and a comparison with other serotypes.
A. Schematic showing the distribution of transposons, Tcn1–Tcn6, in the presumptive centromeres of all 14 chromosomes of C. neoformans strain H99. Each region was identified as the largest ORF-free region on its respective chromosome and contains transposons or its footprints, which are clustered in these sites. B. A comparative analysis of the largest ORF-free regions predicted to be centromeres between C. neoformans var. grubii (H99), C. neoformans var. neoformans (JEC21 and B3501A), and C. gattii (WM276 and R265) using FungiDB reveal conserved synteny of the flanking genes in chromosome 14. The grey color represents the regions that show synteny among different strains. The ORFs present in the centromeric regions are either pseudogenes or have similarity with transposons. C. ChIP-Seq analysis showed the enrichment of a conserved kinetochore protein, CENP-C, at the centromeric regions. Here, the enrichment on centromeric region of chromosome 14 (CEN14) is shown. The upper panel shows the enrichment on the whole chromosome. In the lower panel, the putative centromeric region is enlarged to show the enrichment profile of CENP-C. D. RNA-Seq analysis reveals the absence of poly(A) RNA from CEN14. E. Targeted truncation mutagenesis on either side of the CEN14 centromere DNA. Four DNA fragments were produced and transformed into a diploid strain of C. neoformans. The stick-and-ball represents the telomeric seed sequence added to the constructs by amplification with primer GI003. No targeted recombination was observed for two constructs, whereas the other two PCR analyses indicated integration of the DNA in those regions. F. PCR confirmation of recombination. Lanes 1–3 contain PCRs with primers ai270-GI033, and lanes 5–7 contain PCRs with primers ai270-GI034. Lanes 1 and 5 are amplification results from the diploid strain AI187; lanes 2 and 6 are from strains with integration on the left and right sides, respectively; and lanes 3 and 7 are negative PCR controls. Lane 4 is the Invitrogen 1 kb+ size marker.