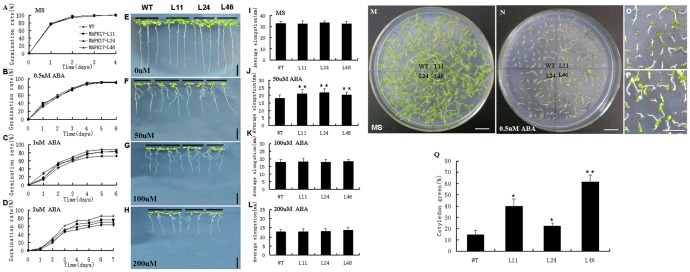
Figure 5. Assays of seed germination and root growth of transgenic Arabidopsis expressing GhMPK17 under abscisic acid (ABA) treatment.
(A to D) Seed germination rate of GhMPK17 overexpression transgenic lines and wild type on MS medium containing different concentrations of ABA. Each curve represents an average of three replicates. (E to H) Phenotype of wild type and GhMPK17 overexpression seedlings under ABA treatment. Seeds were germinated on MS medium under normal condition for 7 days and then the seedlings were transferred and cultured on MS medium supplemented with 0, 50, 100 and 200 µM ABA for 7 days. Each experiment was repeated at least three times with identical results. Bars = 1 cm. (I to L) Statistical analysis of root elongation of wild type and GhMPK17 overexpression plants. Seeds were germinated on MS medium under normal condition for 7 days, and then the seedlings were transferred and cultured on MS medium with 0, 50, 100 and 200 µM ABA for 7 days. Data were shown from three independent experiments. (M and N): Post-germination seedling establishment analysis of GhMPK17 overexpressing plants. (M) Seedlings of wild type and GhMPK17 transgenic lines grew on MS medium without ABA for 10 days. (N) Seedlings of wild type and GhMPK17 transgenic lines grew on MS medium with 0.5 µM ABA for 10 days. (O and P) Partial magnified drawing of wild type (O) and transgenic line 46 (P) in N. Bars = 1 cm. (Q) statistical analysis of the cotyledon greening/expansion ratio of wild type and transgenic seedlings grown on MS medium containing 0.5 µM ABA. *, P<0.05 and **, P<0.01. WT, wild type; L11, L24 and L46, GhMPK17 transgenic line 11, 24 and 46.