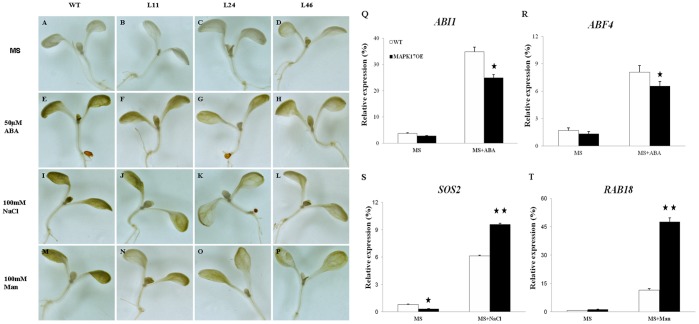
Figure 8. Assays of H2O2 accumulation and the expression levels of ABA- and abiotic stress-related genes in GhMPK17 overexpression transgenic Arabidopsis.
(A to P) Histochemical assay of H2O2 accumulation in wild type (A, E, I, M) and GhMPK17 transgenic seedlings (B to D, F to H, J to L, N to P) on MS medium (A to D), MS medium supplemented with 50 µM ABA (E to H), 100 mM NaCl (I to L) and 100 mM mannitol (M to P). (Q to T) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of expression of ABA-related genes (Q and R) and abiotic stress-related genes (S and T) in wild type and GhMPK17 transgenic seedlings. Total RNA was isolated from two-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings grown under normal conditions (MS) and under ABA (MS+ABA), NaCl (MS+NaCl), mannitol (MS+Man) treatments for 6 h. Relative value of the expression of ABI1, ABF4, SOS2 and RAB18 in Arabidopsis was shown as percentage of AtACTIN2 expression activity. Mean values and standard errors (bar) were shown from three independent experiments. *, P<0.05 and **, P<0.01. WT, wild type; L11, L24 and L46, GhMPK17 overexpression transgenic line 11, 24 and 46; MAPK17OE, GhMPK17 overexpression transgenic lines.