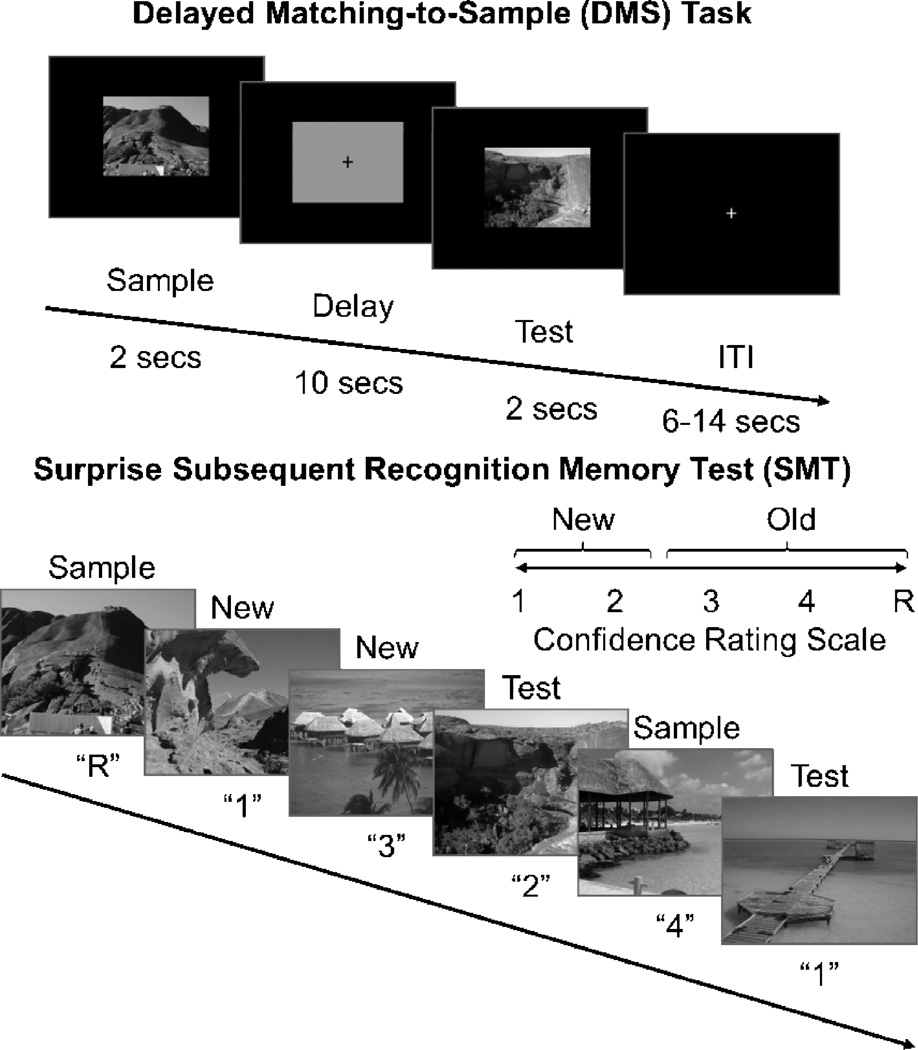
Figure 1.
Recognition memory task. Adapted from Schon et al. [20], participants were first shown a series of 144 pseudo-randomized, trial unique but content similar outdoor scenes in the context of a delayed match to sample (DMS) working memory paradigm. Approximately 15 minutes later, participants were administered a surprise subsequent memory test (SMT) where they were shown all 144 DMS images, plus 144 lure images, and asked to rate their recognition confidence. Participants were blind to the ratio of old to new images.