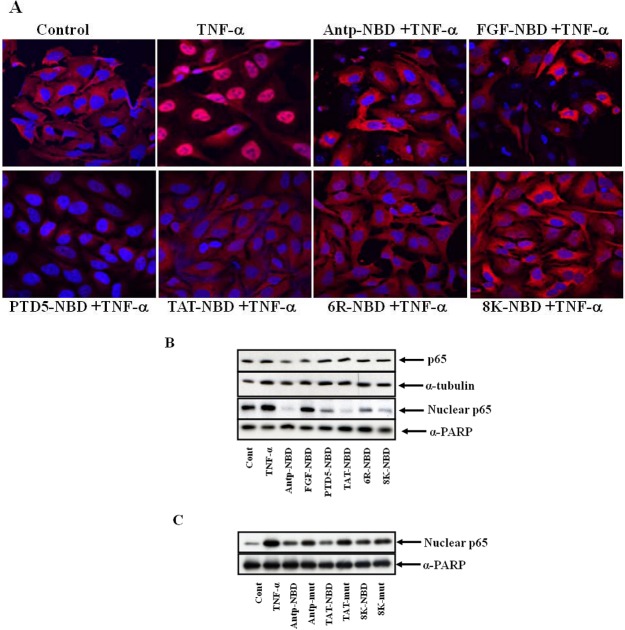
Figure 4.
Inhibition of p65 translocation with NBD peptides. Panel A showing immunohistolochemical analysis of inhibition of p65 nuclear translocation with PTD NBD peptides. HeLa cells were incubated with the 100 µM of PTD-NBD peptides for 1 h, then stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/mL) for 3 h or left untreated. The cells were fixed and immunostained for p65 (red) with nucleus counter stained (blue). (Panel B): Panel B and C showing western blot analysis of PTD-NBD peptide inhibition of TNF-α activated NF-κB binding to nucleus. 293 cells were incubated with 100 µM of PTD NBD peptides for 30 min and subsequently exposed to 10 ng/mL of TNF-α for 1h or left untreated as indicated. Cell extracts were prepared, and nuclear and cytosolic proteins separated as described in methods. The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-p65 antibodies, and alpha tubulin (cytoplasmic loading control) and PARP (nuclear loading control). To confirm the NBD sequence is responsible for NF-κB suppression, 293 cells were incubated with 100 µM of PTD NBD peptides (either WT or mut attached to various PTDs) for 30 minutes and subsequently exposed to 10 ng/mL of TNF-α for 1h or left untreated as indicated (Panel C). Nuclear cell extracts were prepared, and the proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with p65 and PARP, as a loading control, antibodies.