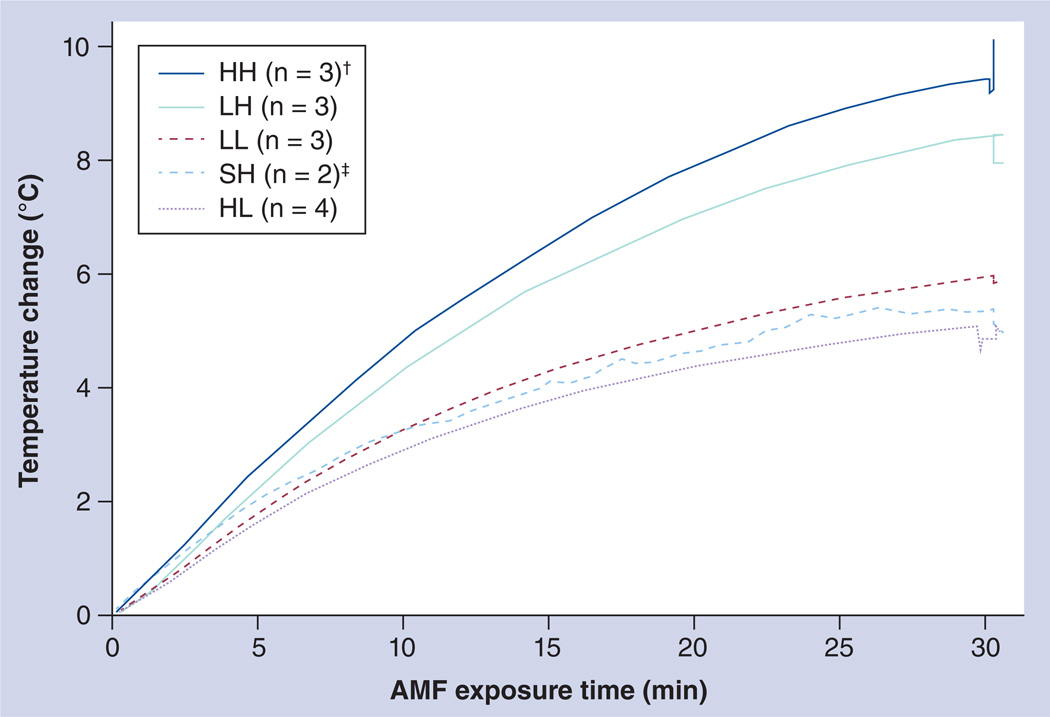
Figure 3. Measured mouse rectal temperatures.
Mice were exposed to an AMF at 140–160 kHz for a period of 30 min, during which rectal temperatures were measured. The y-axis illustrates temperature change, which is defined as Tmax − Tinitial (averaged maximum rectal temperature – averaged rectal temperature at time point 0) for each mouse group. The first letter of each group designation indicates the dose of nanoparticles injected: saline (S), low-dose (L) or high-dose (H) superparamagnetic iron oxide. The second letter of each group designation indicates the field strength for AMF exposure: low (L) or high (H) field.
†Three mice were assigned to the HH group. Two of these mice perished during AMF exposure.
‡Four mice were used for histological and laboratory analysis for the SH group. However, rectal temperature data were only available for two of these mice (n = 2).
AMF: Alternating magnetic field.