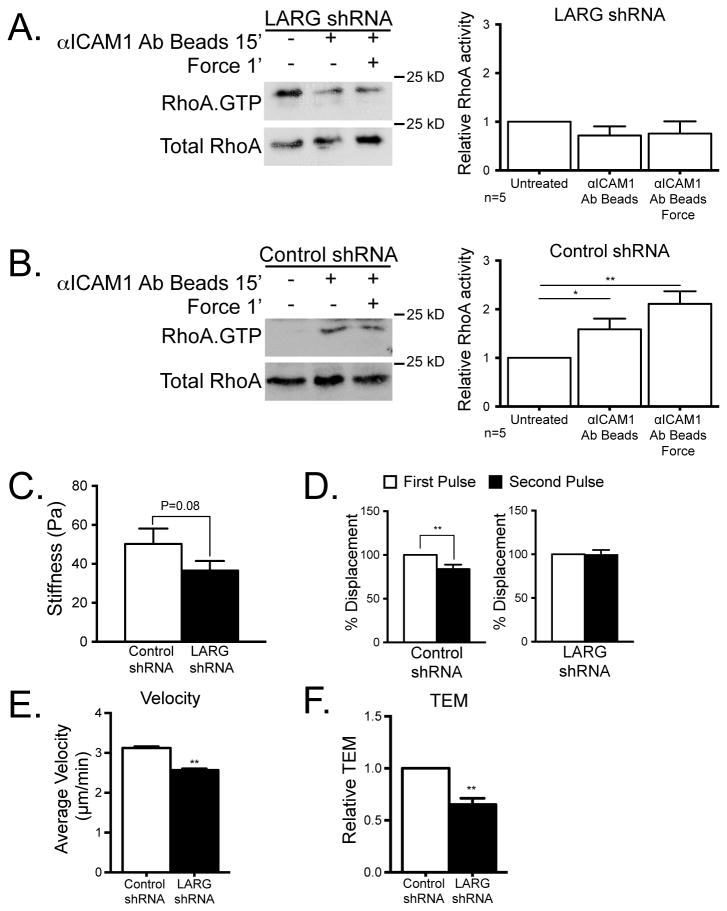
Figure 5.
LARG mediates EC response to mechanical force on ICAM-1 and affects neutrophil crawling and TEM. HUVECs were treated with control (B and C) or LARG (A and C) shRNA lenti-virus for 48 h and selected with 2.5 ng/ml puromycin for 24 h, then TNF-treated overnight. (A and B) RhoA activity was determined by immunoblotting after ICAM-1 clustering with or without force in HUVECs (left) and quantified (right). The means ± SEM of ≥4 independent experiments are shown. Asterisk shows p-value of statistical significance by t test (*, p≤0.05). (C) The stiffness of HMVECs was measured using magnetic tweezers and magnetic beads coated with ICAM-1 mAb. (D) Relative displacement of magnetic beads coated with ICAM-1 mAbs was measured in control HMVECs or in HMVECs in which LARG expression had been knocked down. The means ± SEM of N≥15 independent bead pulls are shown. Asterisk shows p-value of statistical significance by t test (p≤0.01). (E and F) Neutrophils were added to a monolayer of TNF-treated HMVECs after LARG expression had been knocked down. (E) Neutrophils were imaged as they migrated over the HMVEC monolayer surface and their velocity was measured using tracking software. Data are the average of 3 experiments with ≥15 neutrophils measured per experiment. (F) The passage of neutrophils across a confluent EC monolayer was measured using transwell tissue culture inserts. Data are the average of 3 experiments each performed in duplicate. The means ± SEM are graphed. Asterisk shows p-value of statistical significance (*, p≤0.05; **, p≤0.01).