Fig.7.
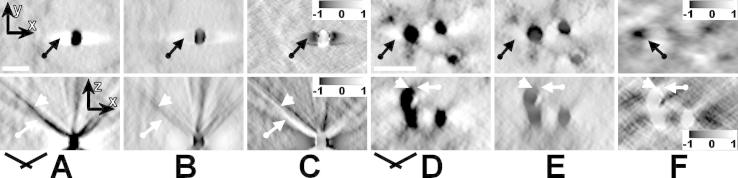
Angular filtering of colloidal gold markers. Top row: x–y cross-sections through reconstructed gold particles, bottom row: x–z cross-sections through the gold particles. (A) Cross-sections of a 20 nm colloidal gold ball obtained from the cerebellum molecular layer prior to angular filtering, (B) after angular filtering. (C) Intensity difference (B)–(A) normalized to <−1, 1>. Black arrows in the top row indicate reduction of intensity in the side maxima, white arrows in the bottom image reduction of the ray artefacts. The angular filter used was bfly65-4-0.2-24-4-10. (D) Cross-sections of a 20 nm silver-enhanced colloidal gold ball through the reconstruction of the immunolabeled Rings & Rods structures prior to angular filtering, (E) after angular filtering. (F) Intensity difference (E)–(D) normalized to <−1, 1>. Black arrows in the top row indicates reduction of the side maxima, white arrows in the bottom image reduction of the ray artefacts. White arrowheads indicate positions where the boundary of the gold particle was smeared due to filtering with an angular filter with a tight central stripe. The angular filter used was bfly24-4-0.2-8-4-4. Scale bars: 50 nm.
