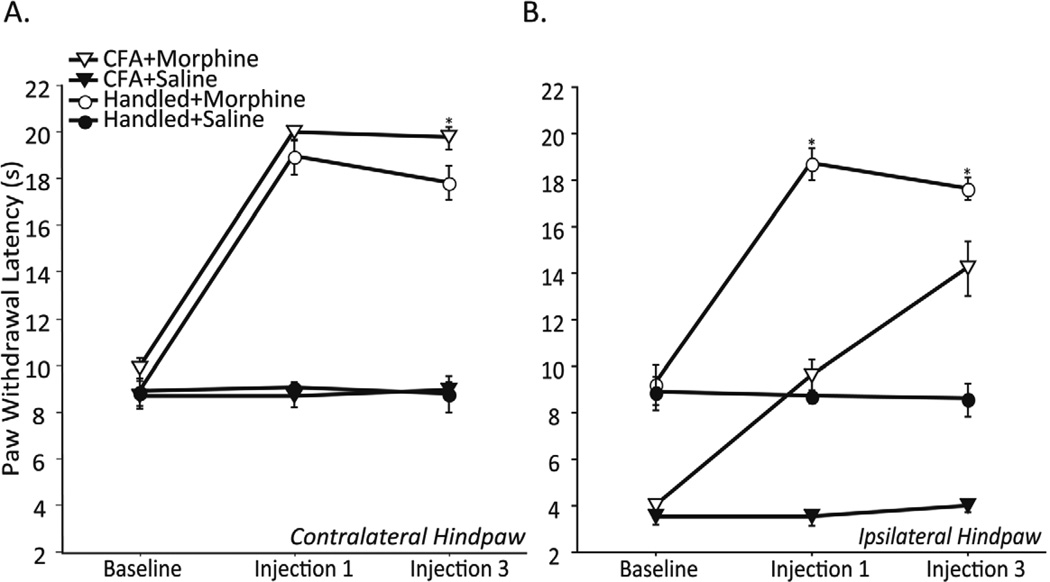
Figure 1.
Contralateral (A) and ipsilateral (B) PWL (in seconds) following intraplantar CFA or handling (Baseline), and after the first and third injection of morphine or saline in CFA+Morphine (n=6), CFA+Saline (n=7), Handled+Morphine (n=6), and Handled+Saline (n=5) treated male rats. The first and third injection of morphine caused an increase in contralateral and ipsilateral PWL as compared with saline controls (p< 0.05; A & B, respectively). Contralateral PWL did not differ between CFA+Saline and Handled+Saline groups at any time point (p> 0.05; A). CFA treatment caused a significant decrease in ipsilateral PWL at all time points as compared with handled controls (p< 0.05; CFA+Saline; Handled+Saline; B). While uninjured animals treated with morphine showed a decrease in analgesia to the third injection as compared with the first (p< 0.05; A), CFA treated animals showed an increase in antihyperalgesia to the third injection (p< 0.05; B). Asterisks indicate significant differences between CFA+Morphine and Handled+Morphine groups.