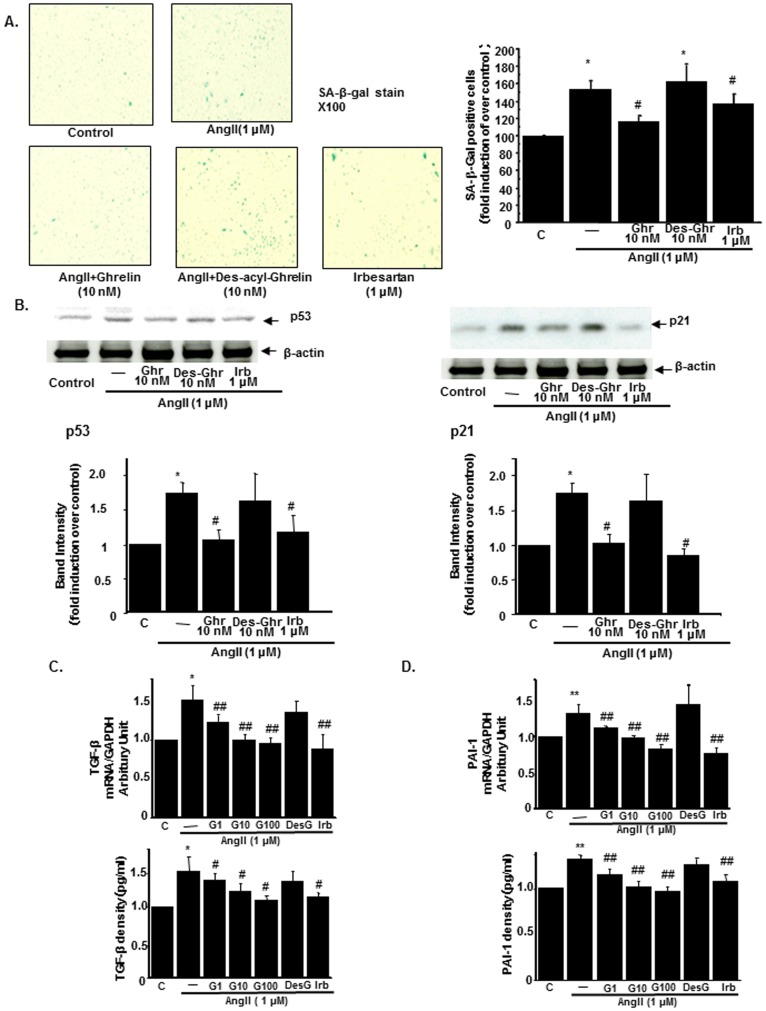
Figure 5. The amelioration of cellular senescent changes in AngII-treated HK-2 by Ghrelin.
(A) Representative staining of senescence-associated β-Galactosidase (SA β-Gal) in untreated HK-2 cells (control), AngII-treated HK-2 cells (AngII, 1 µM), and AngII-treated with the pretreatment of 10 nM Ghrelin (AngII+Ghrelin), 10 nM Des-acyl-Ghrelin (AngII+Des-acy-Ghrelin), or 1 µM AngII type 1 receptor antagonist, irbesartan (left panel). Bar graphs represent the quantification of stained cells (right panel). (B) The protein expressions of p53 (left) and p21 (right) in HK-2 cells. The representative immunoblotting (upper panel) and the results of densitometry analysis (lower panel) were shown. (C) The expression of TGF-β mRNA in HK-2 cells (upper panel) and the concentration of TGF-β in the medium of HK-2 cells (lower panel). (D) The expression of PAI-1 mRNA in HK-2 cells (upper panel) and the concentration of PAI-1 in the medium of HK-2 cells (lower panel). C; control cells, AngII; HK-2 cells treated with 1 µM of AngII, G1, G10, G100; HK-2 cells treated with 1 nM, 10 nM, and 100 nM of Ghrelin, respectively, Des-G; HK-2 cells treated with 10 nM of Des-acyl-Ghrelin, Irb; HK-2 cells treated with 1 µM of irbesartan **p<0.01 vs. control HK-2 cells, *p<0.05 vs. control HK-2 cells, ##p<0.01 vs. AngII-treated HK-2 cells, #p<0.05 vs. AngII-treated HK-2 cells, n = 8.