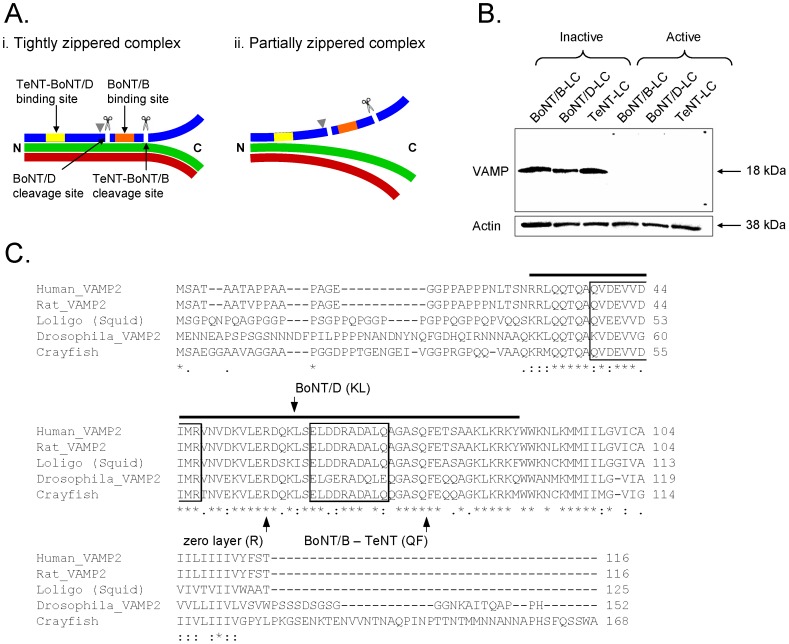
Figure 1. Susceptibility of VAMP to Clostridial neurotoxins.
A, Zippered states of the SNARE complex. Ai, SNARE complex tightly zippered beyond the zero-layer indicated by gray arrow head. VAMP (blue) is protected from cleavage because the binding (yellow and orange bars) and cleavage (scissors and white lines) sites of VAMP-specific Clostridial neurotoxins (TeNT, BoNT/B and BoNT/D) are occluded. Aii, Partially zippered SNARE complex. The binding sites of TeNT and BoNT/D are occluded but the binding and cleavage sites for BoNT/B are exposed such that VAMP is susceptible to cleavage. Green – syntaxin, red – SNAP25 (represents both SNARE binding motifs). B, Clostridial neurotoxins cleave crayfish VAMP in-vitro. Crayfish CNS protein sample was incubated with inactive or active neurotoxins (BoNT/B-LC (0.5 µg/μL), BoNT/D-LC (0.3 µg/μL) and TeNT-LC (0.5 µg/μL)) and stained for neuronal VAMP. The protein bands of 18 kDa represent VAMP. Cleaved VAMP does not appear on the blot when active neurotoxins were used because the VAMP antibody binds only to the uncleaved VAMP protein. Actin staining of 38 kDa below the VAMP blot shows that equal amounts (10 µg) of protein were loaded in each lane. C, Comparison of full-length crayfish VAMP amino acid sequence with VAMP sequences from other species. Crayfish VAMP is similar to VAMP from other species, especially in the conserved SNARE motif region (black bar). The cleavage sites of VAMP-specific neurotoxins are indicated in the alignment. The primary binding sites of the neurotoxins used in this study are indicated as boxed regions (V1 motif (aa 38–47) – TeNT and BoNT/D; V2 motif (aa 62–71) – BoNT/B) based on the human VAMP sequence [29]–[31]. The multiple protein sequence alignment was performed using the online ClustalW2 Multiple Sequence Alignment tool (European Molecular Biology Laboratory - European Bioinformatics Institute, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/).