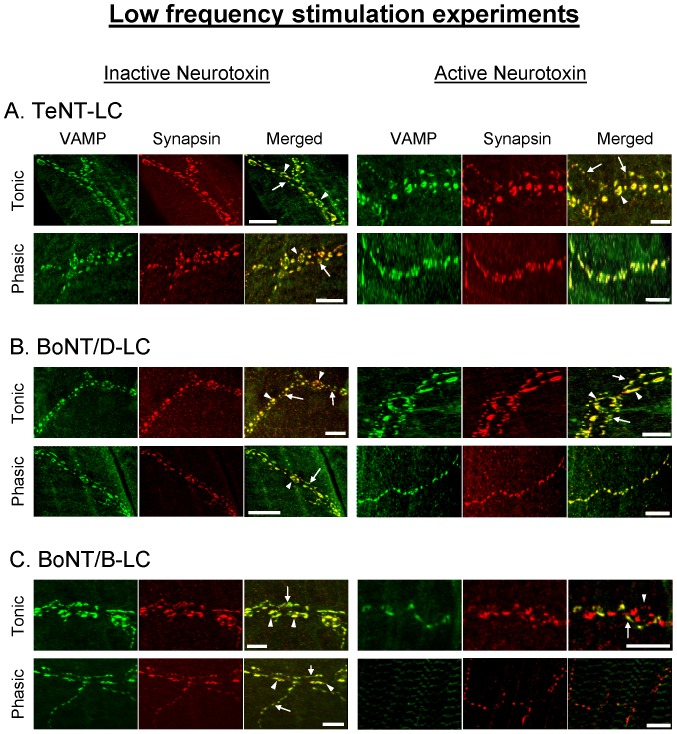
Figure 5. VAMP in phasic and tonic axonal terminals is susceptible only to BoNT/B-LC under low frequency stimulation.
Immunostaining of VAMP and synapsin after the injection of inactive and active TeNT-LC (A), BoNT/D-LC (B) and BoNT/B-LC (C) into the phasic or tonic axon during the low frequency stimulation experiments. In A-C, arrows denote phasic terminals and arrow heads denote tonic terminals. The yellow areas in the merged image represent an overlap of VAMP and synapsin immunoreactivity. In C, the injected boutons contain only synapsin indicating that active BoNT/B-LC cleaved VAMP under low frequency stimulation. Note that only active BoNT/B-LC reduced VAMP immunoreactivity under low frequency stimulation conditions. In B,C, no tonic terminals were present in the phasic image with active neurotoxin. Scale bars – A and B: 19 µm; C: 10 µm.