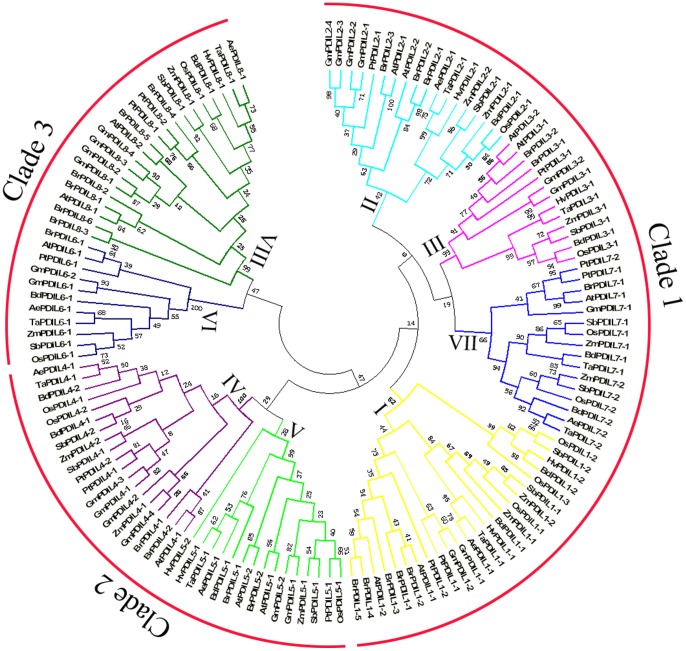
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree showing relationships between the deduced amino acid sequences of 137 PDI and PDI-like genes from different plant species.
11 from Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), 9 from Triticum aestivum (Ta), 7 from Hordeum vulgare (Hv), 7 from Aegilops tauschii (Ae), 12 from Oryza sativa (Os), 12 from Zea mays (Zm), 21 from Glycine max (Gm), 13 from Arabidopsis thaliana (At), 11 from Sorghum bicolor (Sb), 22 from Brassica campestris (Bc),and 12 from Populus trichocarpa (Pt). Multiple alignments of sequences were performed by ClusalW, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbour-joining (NJ) method and evaluated by bootstrap analysis. Numbers on the main branches indicate bootstrap percentages for 1,000 replicates. The three major clades (1–3) and eight phylogenetic groups (I–VIII) identified in the plant PDI family are highlighted with a red arc and the same color branch, respectively.