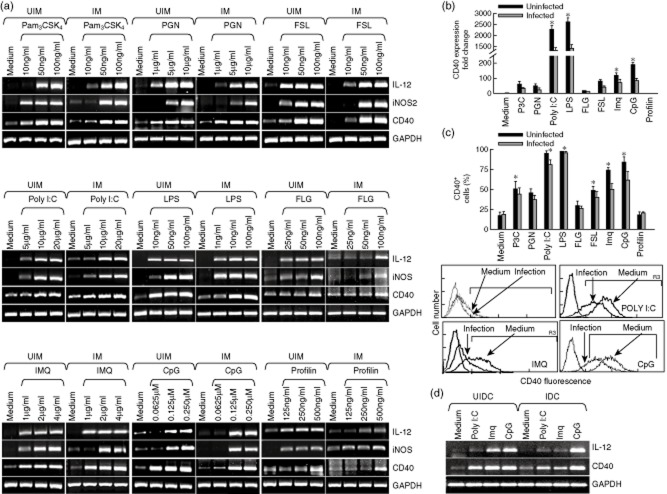
Figure 1.
Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands induce expression of CD40, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and interleukin (IL)-12. Thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal mouse macrophages were harvested and plated. (a) Mouse macrophages were infected with either Leishmania major promastigoes (IM) at a 1:10 macrophage to parasite ratio or left uninfected (UIM), as described in Materials and methods, and were treated with the indicated doses of the TLR ligands: Pam3CSK4, peptidoglycan (PGN), polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [poly( I:C)], lipopolysaccharide (LPS), flagellin (FLG), fibroblast-stimulating lipopeptide (FSL), imiquimod (IMQ), cytosine–phosphate–guanosine (CpG) and Profilin for 8 h, followed by RNA extraction and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to assess the expression of CD40, iNOS and IL-12 (left panel). (b,c) uninfected (UIM) and infected (IM) mouse macrophages were treated with the TLR ligands: Pam3CSK4 (50 ng/ml), PGN (5 μg/ml), poly (I:C) (10 μg/ml), LPS (50 ng/ml), FLG (50 ng/ml), fibroblast-stimulating lipopeptide (FSL) (50 ng/ml), imiquimod (IMQ; 2 μg/ml)), CpG (0·12 μM) and Profilin (250 ng/ml) for 8 h and 24 h, to check the expression of CD40 by real-time PCR (upper right panel) and by fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS) (middle panel), respectively. Expression of CD40 was analysed by FACS in uninfected (medium) and infected (infection) macrophages (lower panel). (d) Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) were treated with poly (I:C) (10 μg/ml), imiquimod (2 μg/ml) and CpG (0·12 μM) for 8 h followed by RNA extraction and reverse transcriptase PCR was performed to assess the expression of CD40 and IL-12p40. UIDC = uninfected BMDC; IDC = infected BMDC. Error bars shown are the mean ± standard error (SE) from three experiments; *P < 0·05.