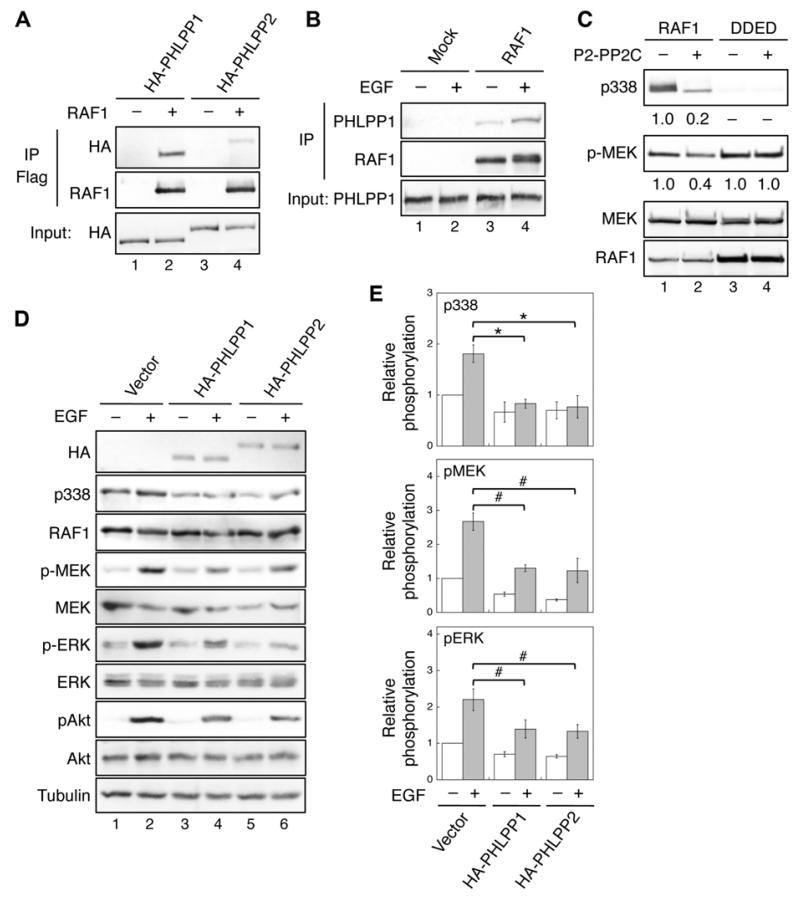
Figure 1. Identification of RAF1 as a substrate of PHLPP.
(A) 293T cells co-transfected with HA-PHLPP1 (lanes 1-2) or HA-PHLPP2 (lanes 3-4) together with vector or Flag-RAF1 were immunoprecipitated with the anti-Flag agarose and analyzed by immunoblotting. The expression of PHLPP1 and PHLPP2 was detected using the HA antibody. (B) 293T cells were serum starved overnight and subsequently treated with EGF (10 ng/ml) for 15 minutes. Cell lysates were incubated with protein A/G beads alone (Mock) or beads plus the RAF1 monoclonal antibody. The presence of PHLPP1 and RAF1 in the immunoprecipitates was detected using the PHLPP1 and RAF1 antibodies, respectively. (C) In vitro dephosphorylation of RAF1. Flag-RAF1 and Flag-RAF1/DDED were incubated with purified PP2C domain of PHLPP2 and subsequently used to phosphorylate recombinant MEK1. The relative phosphorylation of RAF1 and MEK1 were quantified by normalizing to total proteins and shown below the phospho-blots. (D) Stable vector, HA-PHLPP1, or HA-PHLPP2 overexpressing SW480 cells were serum starved overnight and treated with EGF for 15 minutes. Cell lysates were analyzed for phosphorylation and total protein expression. Note that since it was difficult to detect the phosphorylation of endogenous RAF1 at S338 in cell lysates directly, RAF1 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates using the RAF1 antibody. Similar approach was taken to detect S338 phosphorylation in RAF1 in all subsequent experiments. (E) Relative phosphorylation levels of RAF1, MEK and ERK were obtained by normalizing ECL signals of p338, p-MEK and p-ERK antibodies to those of total RAF1, MEK and ERK, respectively. The level in untreated control cells was set to 1. Data represent the mean ± SEM (n=3, * p<0.01 and # p<0.05 by two-sample t-tests).