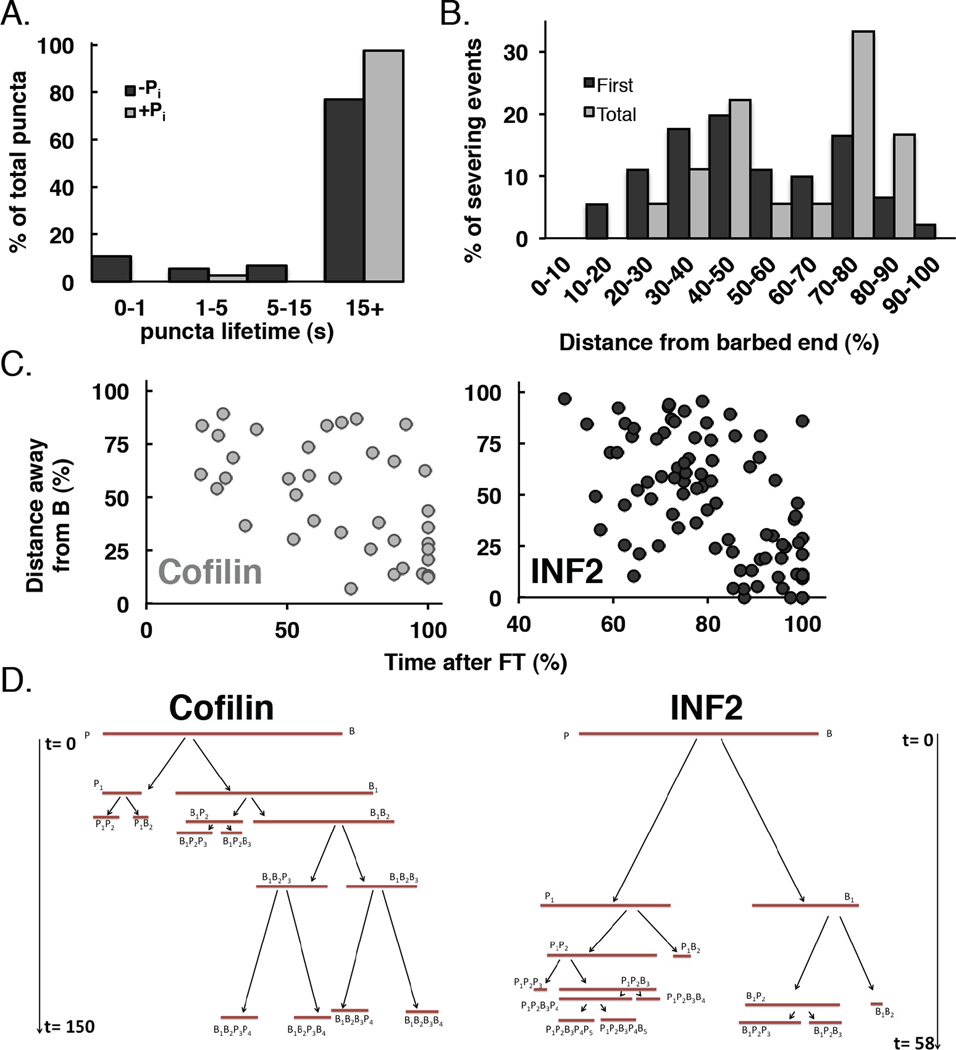
Figure 2. INF2 binds throughout the filament but severs towards pointed end.
(A)Lifetimes of filament-bound puncta in (A). >15s represents puncta that did not dissociate during the observation period (180 sec). n=74 and 39 puncta (13 and 6 filaments) in the absence and presence of phosphate respectively.
(B)Histogram of severing positions for GFP-INF2-FFC (5–20nM) on DDS/F127 treated slides. 18 filaments (91 severing events) quantified (average length 12.3µm, range 5.83–24.22µm at time = 0). Barbed end fragments were measured as a percentage of total filament length.
(C) Correlation of time of severing with respect to distance from original barbed end (as % of original length). n=80 and 38 severing events (11 and 7 filaments) for GFP-INF2-FFC and A488-cofilin, respectively. Filaments were12.5 and 7.86µm mean length (range 6.49–21.59 and 4.55–11.05µm) prior to INF2-FFC or cofilin addition respectively. Severing events were observed for 57.5–112.3 and 68.6–170.8 s after addition of INF2 or cofilin respectively. Note x-axis scale is different between INF2 and cofilin.
(D)Tree map diagraming severing events on individual filaments with time (sec) on the y-axis. t=0 denotes time of cofilin or INF2-FFC addition. B and P denote barbed and pointed ends. Severed filament fragments are named based on severing history with subscripts denoting lineage (B1 being the first barbed end fragment, B1B2 being the second barbed end fragment originating from the first barbed end fragment, and so forth). Original filament lengths: 11.1 (cofilin) and 13.6 µm (INF2). Time and sizes drawn to scale. Additional examples in Figure S2.