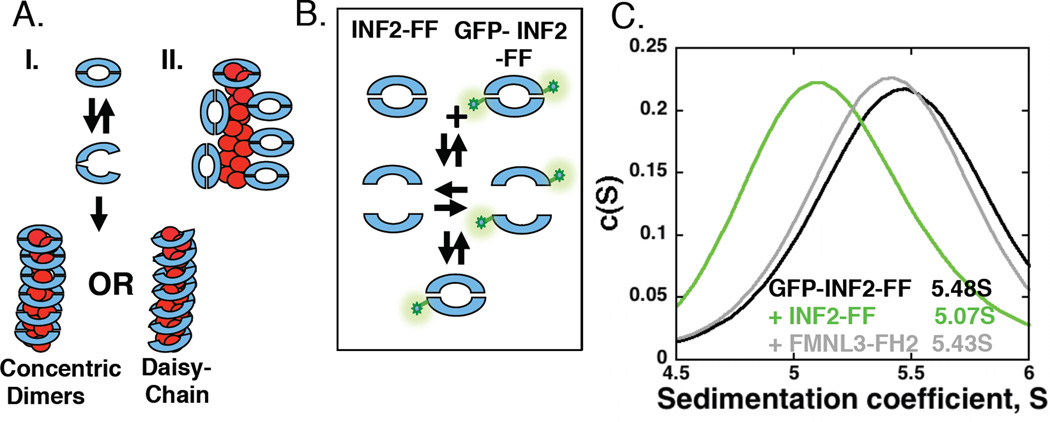
Figure 4. INF2 is a dissociating dimer that binds stoichiometrically to filament sides.
(A)Two models for INF2 binding filament sides. I. FH2 dimer partially dissociates in order to encircle the filament. Encirclement could occur either as concentric dimers or in a daisy-chain, where the lasso-region of one FH2 domain interacts with the post region of an adjacent FH2. II. FH2 dimer binds using interactions between the exterior of the dimer and the filament side. Two possible side-binding orientations shown, as well as a barbed end-bound dimer.
(B) Schematic representation of heterogenous dimer formation in velocity analytical ultracentrifucation experiments. If dimer dissociation is appreciable, a heterogeneous dimer should form upon mixing GFP-labeled and unlabeled FH2 domains, resulting in a shift in S value for the GFP signal.
(C)Velocity analytical ultracentrifugation profiles of GFP-INF2-FF (2µM) alone or mixed with unlabeled INF2-FF (20µM) or FMNL3-FH2 (20µM).