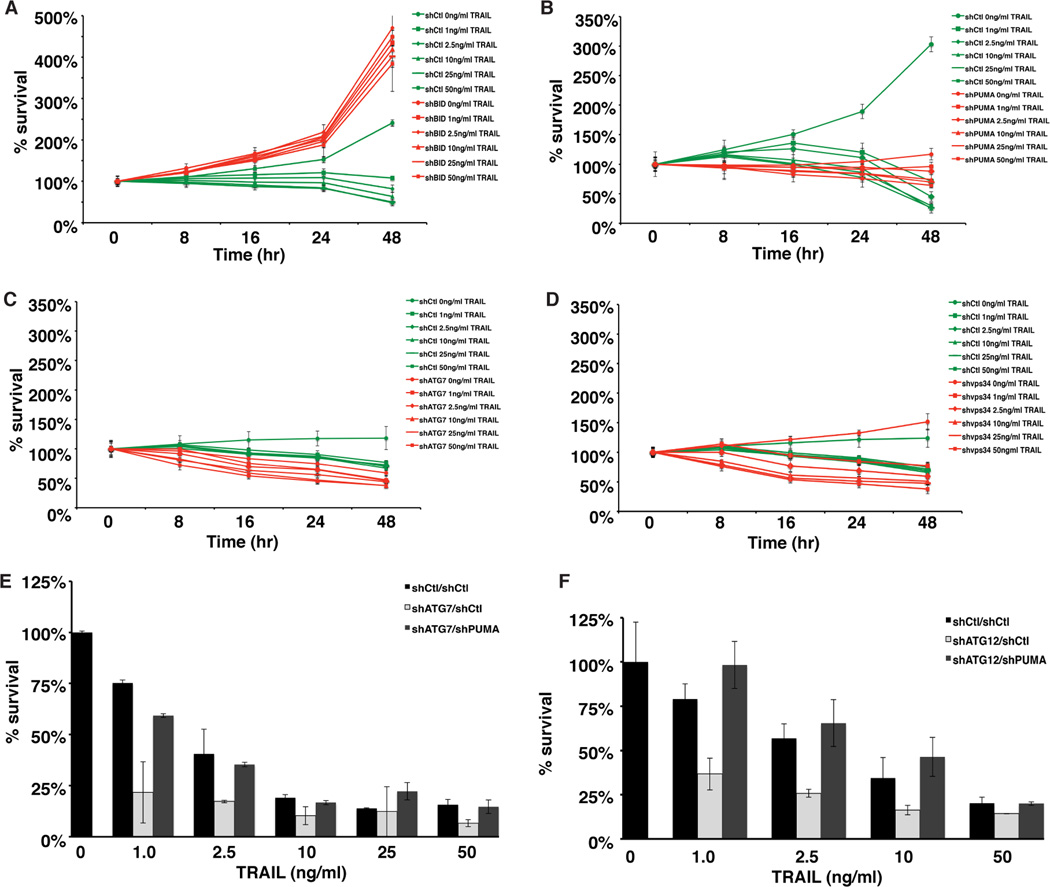
Figure 4. Autophagy regulation of long term cell viability after TRAIL-induced apoptosis is explained by regulation of PUMA.
(A) Quantitation of cell viability by continuous monitoring of mixed populations of control (Green) or shRNA knockdown (Red) cells. HeLa cells were marked with nuclear GFP or mCherry and cell viability after treatment with different doses of TRAIL was determined by continual monitoring using the IncuCyte system. shRNA knockdown of BID completely protects against TRAIL induced death.
(B) shRNA knockdown of PUMA partially inhibits TRAIL induced apoptosis.
(C) shRNA knockdown of ATG7 to inhibit autophagy potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
(D) shRNA knockdown of Vps34 to inhibit autophagy potentiates TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
(E) Cell viability quantified by the IncuCyte at different doses of TRAIL was determined in matched control, ATG7 or ATG7/PUMA knockdown cells. Autophagy inhibition by ATG7 knockdown increases TRAIL induced apoptosis and this is rescued by simultaneous knockdown of PUMA. At higher doses of TRAIL, the protective effect of autophagy inhibition is reduced.
(F) Cell viability quantified by the IncuCyte in matched control, ATG12 or ATG12/PUMA knockdown cells. Autophagy inhibition by ATG12 knockdown increases TRAIL induced apoptosis that is rescued by simultaneous knockdown of PUMA.
See also Supplemental Figures 3 and 4.