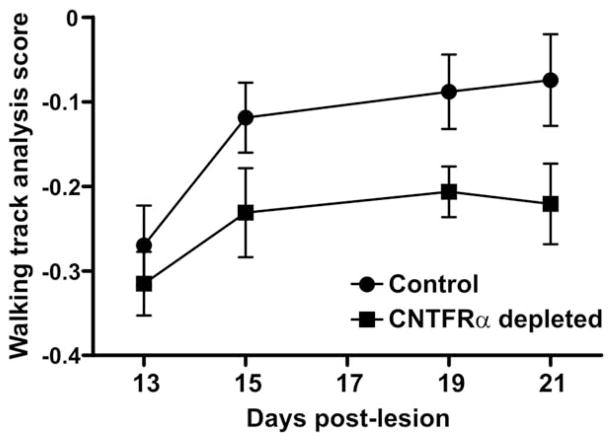
Figure 11.
Depletion of muscle ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor α (CNTFRα) impairs recovery of motor function following nerve lesion. Walking track analysis revealed that the muscle CNTFRα-depleted mice display impaired motor function recovery following sciatic nerve crush, relative to controls (P <0.003; F =9.71; main effect of muscle CNTFRα depletion in two-way ANOVA; less powerful post hoc individual group comparisons, appropriately designed to protect against cumulative type I error, were unable to detect differences on individual days). “Walking track analysis scores” compare lesioned and control sides within animals such that values increase as the lesioned side leg recovers function to more closely resemble the function of the unlesioned side (see Materials and Methods). Animals were tested in parallel by investigators blind to genotype. Means with SEM bars are presented. Numbers of control mice tested: 13 days post lesion (DPL) 9; 15DPL, 11; 19DPL, 11; 21DPL, 9. Number of muscle CNTFRα-depleted mice tested: 13DPL, 7; 15DPL, 7; 19DPL, 6; 21DPL, 6.