FIGURE 4.
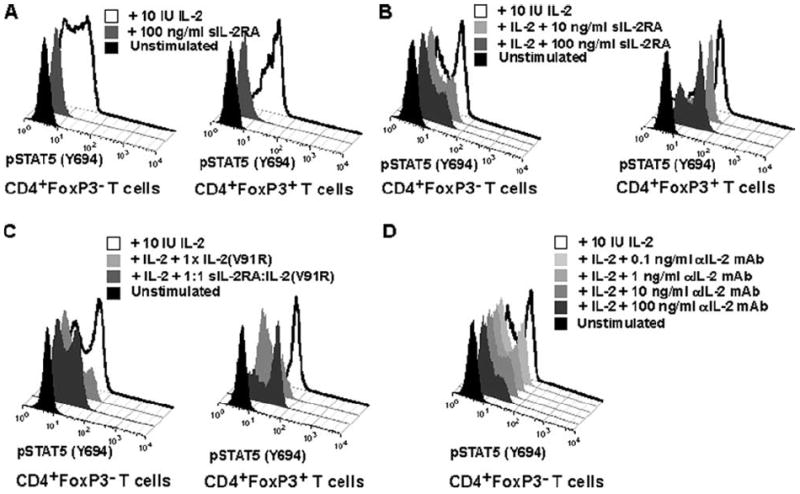
sIL-2RA inhibits IL-2-mediated signaling. A and B, FACS histograms showing pSTAT5 (Y694) phosphorylation in CD4+FoxP3− and CD4+FoxP3+ T cells obtained from fresh ex vivo blood from a healthy human subject. Background levels (black histogram), induction of phosphorylation following stimulation with 100 IU of IL-2/ml (white histogram), as well as the effect of sIL-2RA addition (gray histogram) are shown. Stimulation with IL-2 occurred for 30 min at 37°C. Results are representative of three independent experiments. C, sIL-2RA, complexed with an IL-2 antagonist, can reverse inhibition of IL-2 signaling by an IL-2 antagonist (mutated IL-2). FACS histograms showing pSTAT5 (Y694) phosphorylation in CD4+FoxP3+ in fresh ex vivo blood obtained from a healthy human subject. Background levels (black histogram) and induction of phosphorylation following stimulation with 10 IU of IL-2/ml (4 pM, open histogram) are shown as well as various experimental conditions with sIL-2RA and an IL-2 antagonist (mutated IL-2 V91R5). Mean fluorescence intensity values are: 10 IU IL-2 (39.6); IL-2 plus 1× IL-2 V91R (8.5); IL-2 plus 1:1 sIL-2RA-IL-2 V891R (30.8); unstimulated (5.9). Stimulation with IL-2 occurred for 30 min at 37°C. A 1:1 sIL-2RA:IL-2 (V91R) ratio means that sIL-2RA and IL-2 (V91R) were added in equimolar amounts (400 pM) and preincubated for 30 min at 37°C before addition to whole blood with IL-2. The addition of 1× IL-2 (V91) equals to the addition of 400 pM. Results are representative of two independent experiments. D, For comparison with the effect of sIL-2RA on pSTAT5 signaling, the inhibition of pSTAT5 signaling by a neutralizing anti (α)-IL-2 mAb is shown.
