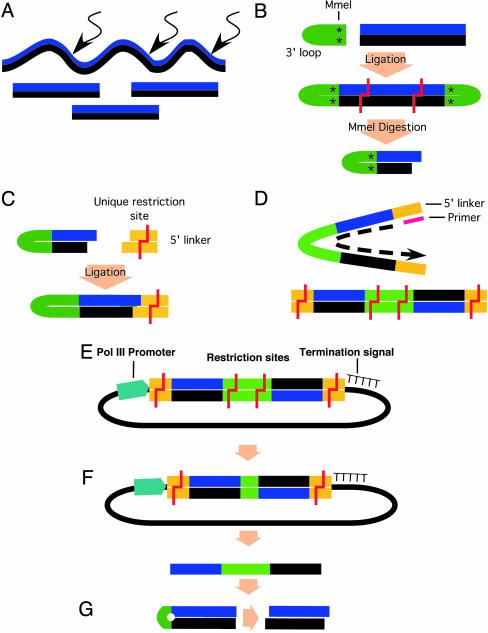
Fig. 1.
Outline for enzymatic production of the siRNA library. (A) Double-stranded cDNA is fragmented by DNase I treatment or by a mixture of restriction endonucleases. (B)A3′ loop (green) linker containing an MmeI site (asterisk) and a unique restriction site that will eventually leave an 8-bp spacer is ligated to the fragments, followed by MmeI digestion. (C) MmeI-digested fragments are ligated to a 5′ linker (yellow) containing a unique restriction site. (D) The single-stranded hairpin is denatured and is converted to linear dsDNA after DNA polymerase synthesis of the second strand. (E) The entire siRNA-like sequence, sense and antisense strands (black/blue) and spacer (green), is ligated into a viral expression vector between a polymerase III promoter and a termination signal (five thymidines). (F) The spacer is minimized to 8 bp in length by digestion with restriction endonuclease and self-ligation of the plasmid. (G) Expression from the polymerase III promoter generates a hairpin-shaped siRNA, which is processed by dicer to give rise to a 21-nt sense and antisense functional siRNA.