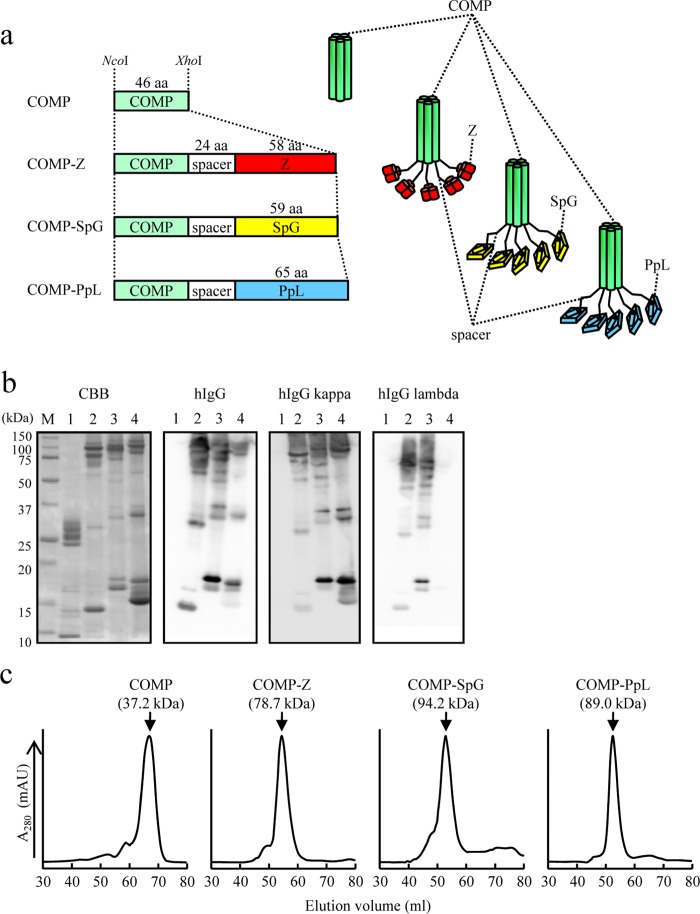
FIG 1.
Expression of the COMP-IBDs. (a) Schematic drawing of the coiled-coil domain of the cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) fused to immunoglobulin-binding domains (IBDs). The coiled-coil domain (green) is fused to the Z domain (red), a derivative of the B domain of Staphylococcus aureus protein A; the B domain of group G Streptococcus protein G (yellow); or the B domain of Peptostreptococcus magnus protein L (blue). The fusion proteins contain a 24-amino-acid (aa) spacer region between the coiled coil and the IBD. The coding sequences of the fusion proteins were placed between the NcoI and XhoI sites of pET-22b and thus were expressed as pelB fusion proteins for secretion from Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). The COMP and COMP-Z constructs were engineered in our previous study (12). (b) Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE; 15%) of nickel-affinity-purified COMP (lanes 1), COMP-Z (lanes 2), COMP-SpG (lanes 3), and COMP-PpL (lanes 4). The protein bands were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) or subjected to Western blotting and then reacted with hIgG or hIgG containing the kappa or lambda light chain. For Western blotting, horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated antibodies were directly applied to the membrane to detect the COMP-IBD fusion proteins. Lane M, molecular mass marker. (c) COMP or the COMP-IBDs were subjected to size exclusion chromatography. Their estimated molecular masses, based on the standard protein marker, are indicated in parentheses.