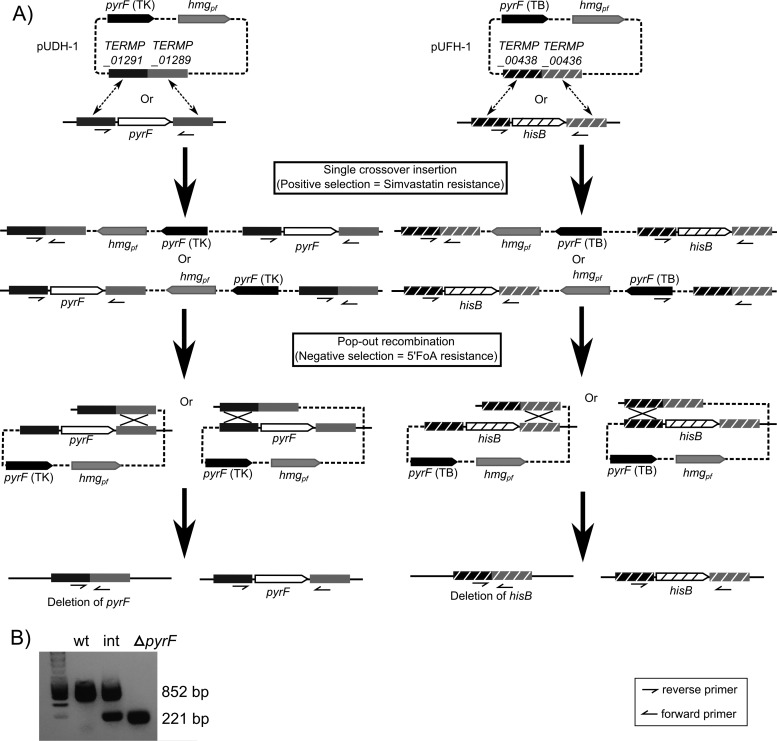
FIG 2.
Deletion pathway of pyrF and hisB genes. (A) Two suicide vectors were constructed to ligate homologous-region amplification (TERMP_01289, TERMP_01291, TERMP_00436, and TERMP_00438) with pUFH or pUDH. The plasmids used were pUDH-1 and pUFH-1. After transformation, the plasmid was integrated into the genome by a first crossover event in the homologous-region fragment. The second step was the pop-out recombination (or excision) event. There are two possibilities: a recombination between the other homologous fragments, resulting in the deletion of the targeted gene, or a recombination between the same homologous fragments of the first recombination, which gives the WT genotype. pyrF was deleted from strain UBOCC-3107 (WT), and hisB was deleted from strain UBOCC-3256 (ΔpyrF). (B) To verify the different genotype configurations, PCR amplification was performed with the primers matching the HR1 and HR2 regions: XhoI-pyrF-TB-Up and SmaI-pyrF-TB-Do for pyrF deletion and Verif-hisB-Up and Verif-hisB-Do for hisB deletion (data not shown).