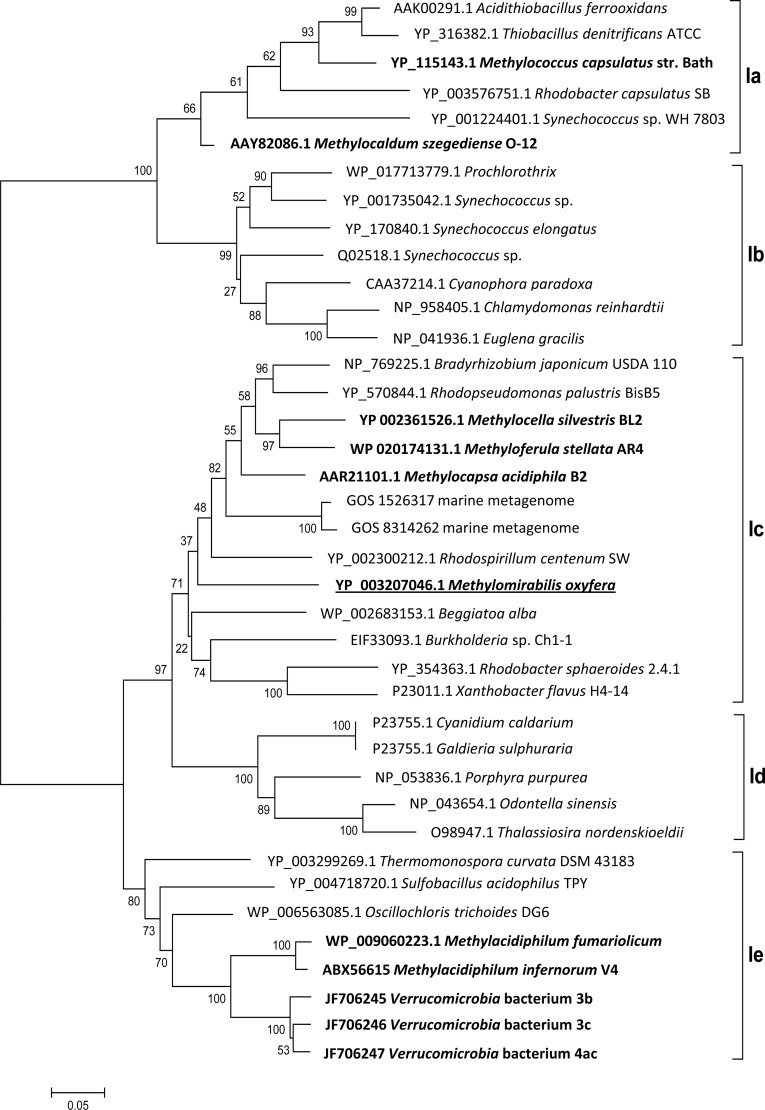
FIG 2.
Bootstrap consensus tree of selected RubisCO form I sequences calculated from 1,000 replicates. The evolutionary history was inferred using the neighbor-joining method, and the evolutionary distances were determined using the Dayhoff matrix. The scale bar represents the number of amino acid changes per site. The alignment gaps were eliminated in a pairwise comparison. RubisCO sequences of methanotrophs are highlighted in bold, and the sequence of “Ca. Methylomirabilis oxyfera” is underlined. The classification is based on a previous study (55), with types Ia and Ib belonging to the green-like RubisCOs and types Ic, Id, and Ie belonging to the red-like RubisCOs.