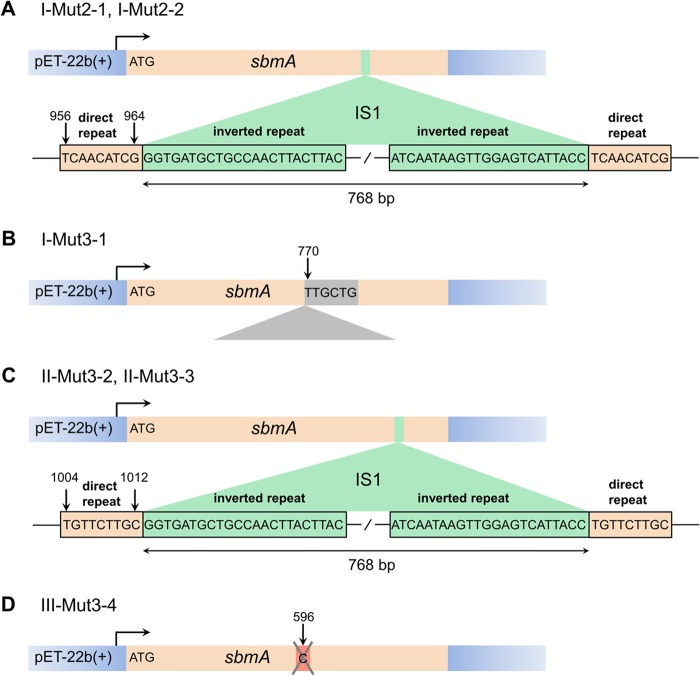
FIG 5.
Mutations in the sbmA gene sustained by the recombinant sbmA-pET-22b(+) plasmid when gene expression was induced in the presence of pyrrhocoricin. (A) Disruption of the sbmA coding region by the 768-bp transposon insertion (E. coli insertion sequence 1 [IS1]) between positions 956 and 964 in clones I-Mut2-1 and IMut2-2. The sequences of 9-bp direct repeats of the target sequence, originating from the insertion, and the 23-bp inverted repeats at the IS1 termini are shown. (B) sbmA gene disruption by a sequence of unknown origin inserted in the coding sequence before nucleotide 770 in clone I-Mut3-1. (C) The IS1 transposon inserted between positions 1004 and 1012 of the sbmA coding region in clones II-Mut3-2 and II-Mut3-3. (D) A single-base deletion in sbmA identified in clone III-Mut3-4.