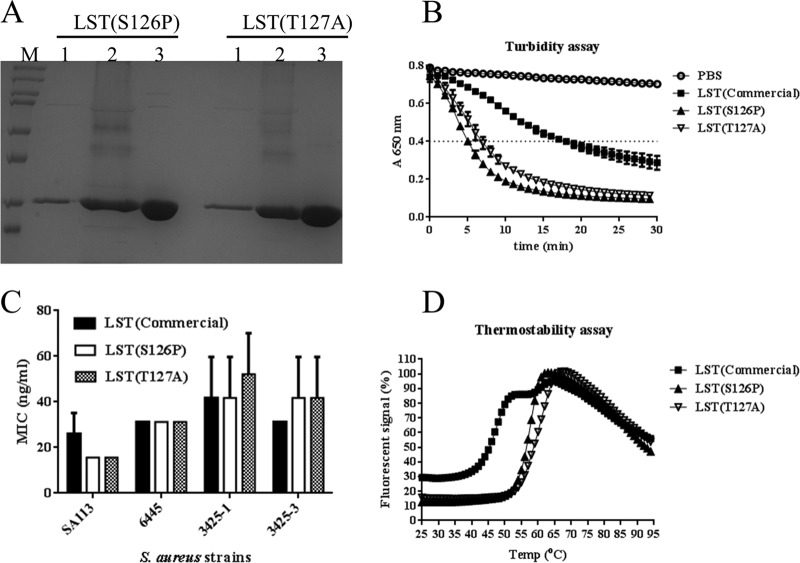
FIG 6.
Detailed analysis of aglycosylated LST variants. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of enzyme expression and purification. Lanes: M, marker; 1, 10 μl of supernatant from shake flask culture; 2, 10 μl of supernatant from bioreactor culture; 3, 10 μg of purified protein. (B) Kinetic analysis of S. aureus lysis in microplate turbidometric assays. The horizontal line provides a visual guide to assess TOD50. (C) Antibacterial efficacy as measured by MIC assay. An S. aureus laboratory strain (SA113) and three clinical isolates were assessed for growth inhibition by serial dilutions of purified enzymes. The OD650 readings after 24 h of growth show that, while the different strains exhibited different MIC0 values (P = 0.0008, two-way analysis of variance), wild-type LST and the engineered variants did not exhibit significantly different MIC0s for any given strain (P = 0.8281), and neither was there a significant interaction between the different enzyme treatments and different strains (P = 0.6529). (D) Melting temperature analysis by differential scanning fluorimetry. The engineered aglycoslyated variants exhibit a single transition, whereas commercial wild-type LST exhibits two distinct transitions, one at a substantially lower temperature. Error bars represent standard deviations from three experiments.