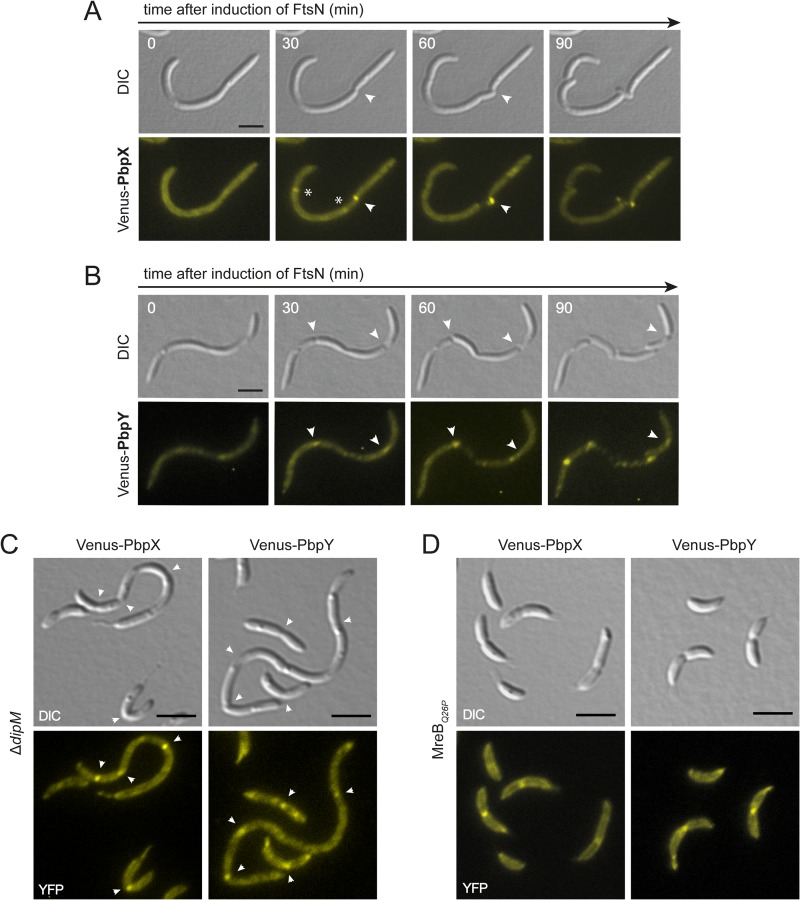
FIG 6.
Midcell localization of PbpX and PbpY is dependent on FtsN but independent of MreB. (A) Effect of FtsN depletion on PbpX localization. Cells of strain AM473 (Pvan::Pvan-ftsN ΔftsN Pxyl::Pxyl-venus-pbpX) were cultivated for 12 h in PYE medium to deplete FtsN. Three hours prior to microscopic analysis, expression of venus-pbpX was induced by addition of 0.3% xylose. The cells were then transferred onto an M2G agarose pad supplemented with 0.3% xylose and 0.3% vanillate to reinduce ftsN expression and imaged at the indicated time points. Arrowheads point to constriction sites. Asterisks indicate Venus-PbpX foci at incipient division sites that fade during the course of the experiment, possibly due to photobleaching. Bar, 3 μm. (B) Effect of FtsN depletion on PbpY localization. Cells of strain AM472 (Pvan::Pvan-ftsN ΔftsN Pxyl::Pxyl-venus-pbpY) were treated and analyzed as described for panel A. Bar, 3 μm. (C) DipM-independent localization of PbpX and PbpY to the cell division site. DipM-deficient cells expressing venus-pbpX (WS058) and venus-pbpY (WS057) from the xylose-inducible xylX promoter were imaged by DIC and fluorescence microscopy. Arrowheads point to constriction sites. Bar, 3 μm. (D) MreB-independent localization of PbpX and PbpY to the division site. Cells of an mreBQ26P mutant expressing venus-pbpX (WS084) or venus-pbpY (WS085) under the control of the xylose-inducible xylX promoter were imaged by DIC and fluorescence microscopy. Bar, 3 μm.