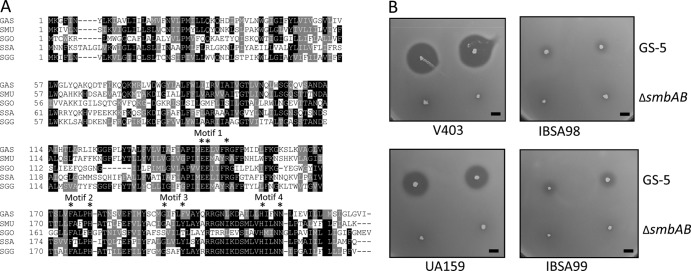
FIG 3.
Deletion of the lsrS homolog in S. mutans makes the strains resistant to Smb-mediated inhibition. (A). Multiple-sequence alignment of LsrS and its homolog from various streptococci. Sequences were aligned by use of the ClustalW program, and the degree of relatedness is displayed with the BoxShade program, where black and gray indicate identical and similar residues, respectively. Sequences were obtained from GenBank (accession numbers are in parentheses). The strains were S. pyogenes (GAS; NP_269484), S. mutans (SMU; NP_721090), Streptococcus gordonii (SGO; YP_001449790), S. sanguinis (SSA; YP_001034746), and S. gallolyticus (SGG; YP_004287423). The four conserved putative metalloprotease motifs along with the active-site residues (asterisks) are also indicated. (B). Deferred antagonism assay using two S. mutans isolates and their mutant derivatives. Assays were carried out with the GS-5 and ΔsmbAB strains as tester strains, as described in the legend to Fig. 1, and repeated at least four times. Bars, 5 mm.