FIG 2.
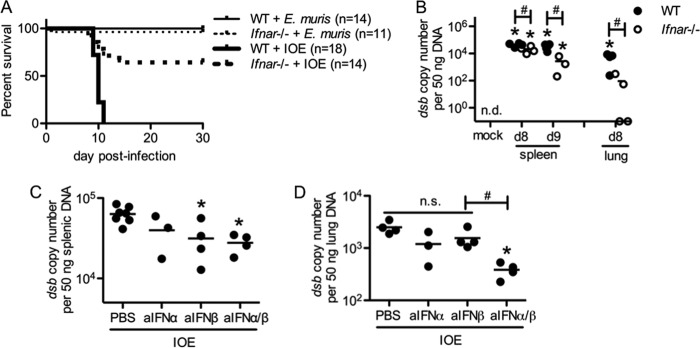
Type I IFNs are detrimental during IOE infection. Survival was assessed and bacterial burden was measured in mice where type I IFN signaling was disrupted. (A) Survival curves of E. muris or IOE-infected WT and Ifnar−/− mice are shown (numbers of mice per group are shown in parentheses). (B) Bacterial burden in the spleens and lungs of IOE-infected WT and Ifnar−/− mice at day 8 and/or day 9 postinfection is shown. Bacterial burden at day 8 postinfection in the spleens (C) and lungs (D) of IOE-infected WT mice that received neutralizing antibodies to IFN-α, IFN-β, or both is shown. Asterisks indicate a significant difference compared to the counterpart mock controls (P < 0.05). Number symbols (#) indicate a significant difference between the groups as indicated (P < 0.05). “n.s.” indicates no significant difference (P > 0.05). “n.d.” indicates not detectable. For the data shown in panels B to D, at least three mice were used for each group.
