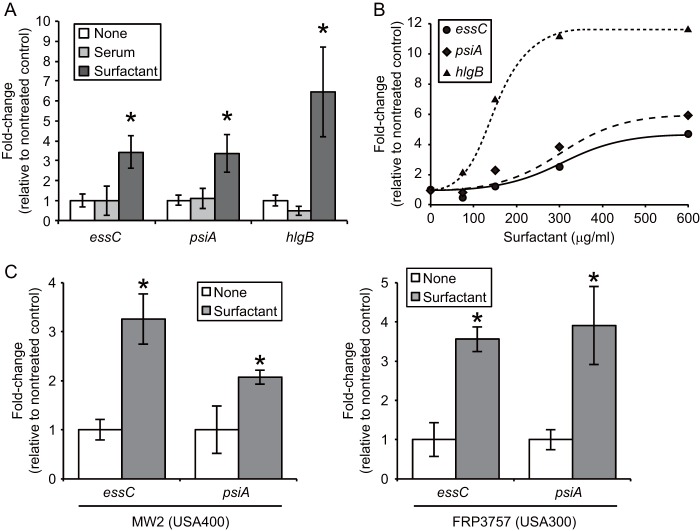
FIG 2.
Pulmonary surfactant-dependent induction of S. aureus essC, psiA, and hlgB genes. (A) S. aureus Newman was cultured in TSB medium containing either 10% serum or 0.3 mg/ml Surfacten to an OD600 of 1. Amounts of essC, psiA, and hlgB mRNAs were determined by quantitative RT-PCR. Each value was normalized to 16S rRNA, and the ratio of the surfactant-treated to the nontreated group was calculated. Data represent means ± standard deviations (SD) for 4 experiments. For each gene, statistical differences compared with the nontreated group were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's multiple-comparison test (*, P < 0. 01). (B) Dose dependency of pulmonary surfactant for the induction of S. aureus gene expression. RNAs were collected from bacteria at an OD600 of 1 and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR analysis. The expression level of each gene was normalized to that of 16S rRNA, and the induction ratio relative to the nontreated group is indicated. (C) Induction of gene expression by pulmonary surfactant in CA-MRSA. MW2 (USA400) and FRP3757 (USA300) were cultured in the presence of 0.3 mg/ml Surfacten to an OD600 of 1, and quantitative RT-PCR analysis of each gene was performed. Data represent means ± SD for 3 or 4 experiments. Statistical differences for each gene compared with nontreated groups were analyzed by Student's t test (*, P < 0.05).