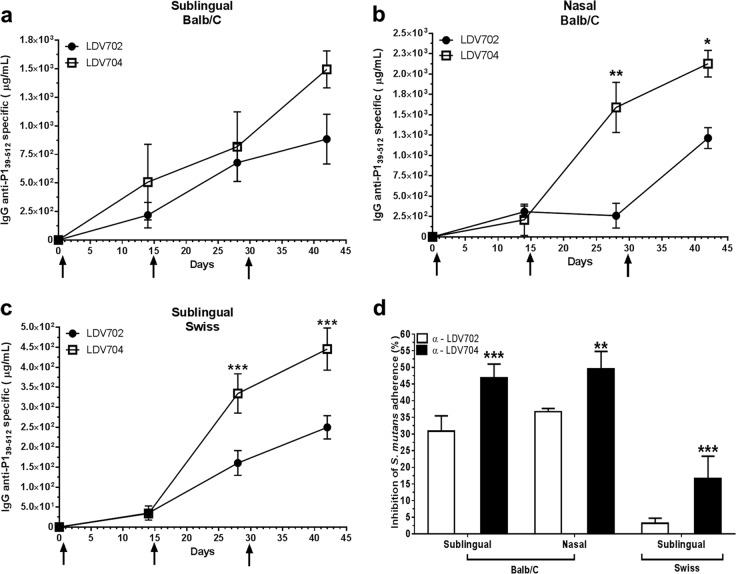
FIG 4.
Antibody responses of mice immunized with B. subtilis spores via the sublingual or nasal route and neutralization of S. mutans SAG-mediated adherence to abiotic surfaces. (a, c) Systemic immune response elicited in BALB/c mice (a) and in Swiss mice (c) after immunization with B. subtilis spores by the sublingual route. (b) Anti-P139-512 IgG antibodies elicited in BALB/c mice immunized with B. subtilis spores by the nasal route. Mice were immunized with 3 single doses (108 spores/dose) of the B. subtilis LDV704 or LDV702 strain (arrows). The P1-specific IgG responses were measured by ELISA with pooled serum samples for the BALB/c mice (n = 5) and serum samples from individual animals for the Swiss mice (n = 10). The results obtained with B. subtilis 1012 were subtracted from the final values for the mice immunized with the vaccine strains. (d) Inhibition of SAG-mediated adhesion of S. mutans by anti-P139-512-specific antibodies. The inhibition of the adherence was determined using the same formula presented in the legend to Fig. 3. All tested serum samples were obtained after the last dose (pool) and were used at the same concentration (2 μg/ml of P1-specific IgG). Immunization groups are indicated in the graph (x axis). The results represent the averages of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistically significant differences compared with the results obtained with the B. subtilis LDV702 strain are indicated (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).