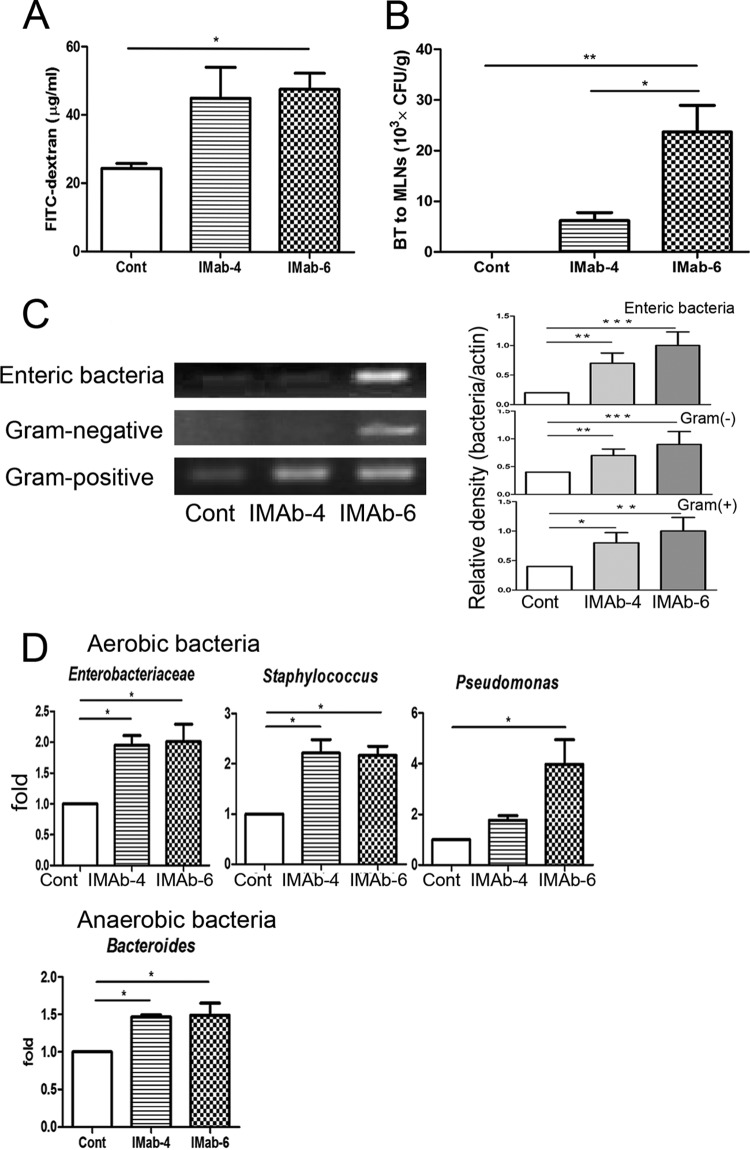
FIG 2.
Antibiotic treatment induced intestinal permeability and bacterial translocation. (A) Antibiotic treatment for 4 days or 6 days significantly increased the intestinal permeability compared with the control group. (B) Antibiotic treatment for 4 or 6 days significantly increased translocation of enteric bacteria to mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) compared with the control group. (C) Antibiotic treatment for 6 days induced a significant increase in the translocation of Eubacteria organisms, enteric bacteria, and Gram-positive and -negative bacteria to MLNs. (D) Antibiotic treatment markedly induced the translocation of members of the Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas, and Bacteroides to MLNs. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; Cont, control; IMab-4, intramuscular antibiotic treatment for 4 days; IMab-6, intramuscular antibiotic treatment for 6 days; BT, bacterial translocation; MLNs, mesenteric lymph nodes. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. n = 4 to 6/group.